Page 280 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 280
280 Mathematica Solutions to Problems
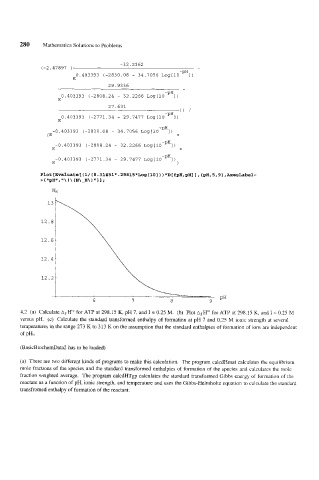
-32.2362
(-2.47897 (
-PH
0.403393 (-2830.08 - 34.7056 LOg[lO I)
E
29.9336
0.403393 (-2808.24 - 32.2266 L~g[lO-~~l)
E
27.631
)) /
0.403393 (-2771.34 - 29.7477 Log[lO-PHl)
E
-PH
-0.403393 (-2830.08 - 34.7056 LOg[lO I) +
(E
-0.403393 (-2808.24 - 32.2266 L~g[lO-~~l)
E
-0.403393 (-2771.34 - 29.7477 L~g[lO-~~l)
E )
Plot[Evaluate[(l/(8.3l45l*.298l5*Log[lO]))*D[fpH,pH]l,{pH,5,9},~esLabel-
> {lmpH1l, ! \ (N\-H\) ''1 I ;
'I\
NH
4.2 (a) Calculate AfHo for ATP at 298.15 K, pH 7, and I = 0.25 M. (b) Plot &Ha for ATP at 298.15 K, and I = 0.25 M
versus pH. (c) Calculate the standard transformed enthalpy of formation at pH 7 and 0.25 M ionic strength at several
temperatures in the range 273 K to 313 K on the assumption that the standard enthalpies of formation of ions are independent
of pH..
(BasicBiochemData2 has to be loaded)
(a) There are two different kinds of programs to make this calculation. The program calcdHmat calculates the equilibrium
mole fractions of the species and the standard transformed enthalpies of formation of the species and calculates the mole
fraction weighted average. The program calcdHTgp calculates the standard transformed Gibbs energy of formation of the
reactant as a function of pH, ionic strength, and temperature and uses the Gibbs-Helmholtz equation to calculate the standard
transfromed enthalpy of formation of the reactant.