Page 284 - Thermodynamics of Biochemical Reactions
P. 284
284 Mathernatica Solutions to Problems
A, H lo
'
6 7 8 9 PH
~lot[(calctrGerx[atph+h20h+de==adph+pih,pH,.251-
calctrGerx[atp+h2o+de==ad~+p~,pH,.251~~.29815,~pH,5,9~,~~sLab~l-
>{ itpHmi, I*\ ! \ (TraditionalForm\' \ (A\-r\) S ' \"O\) "1 1 ;
a, s lo
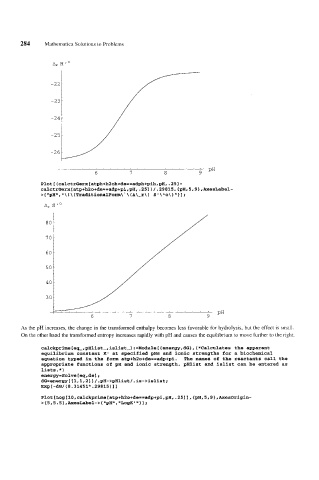
As the pH increases, the change in the transformed enthalpy becomes less favorable for hydrolysis, but the effect is small.
On the other hand the transformed entropy increases rapidly with pH and causes the equilibrium to move further to the right.
calck~rime[eg_,~Hlist~,~slist~l:=Module[{energy,dG},(*Calculates the apparent
equilibrium constant K' at specified pHs and ionic strengths for a biochemical
equation typed in the form atp+hao+de==adp+pi. The names of the reactants call the
appropriate functions of pH and ionic strength. pHlist and islist can be entered as
lists.*)
energy=Solve[eq,del;
dG=energy[[l,l,211/.pH->pHlist/.is->islist;
E~p[-dG/(8.31451*.29815)]1
Plot[Log[lO,calckprime[atp+h2o+de==adp+p~,pH,.25ll,(~H,5,9~,~esOrigin-
> (5,5.5 1, AxesLabel-> ( lmpH1s, "LogK' "1 I ;