Page 217 - Uninterruptible Power Supplies
P. 217
Batteries
Batteries 215
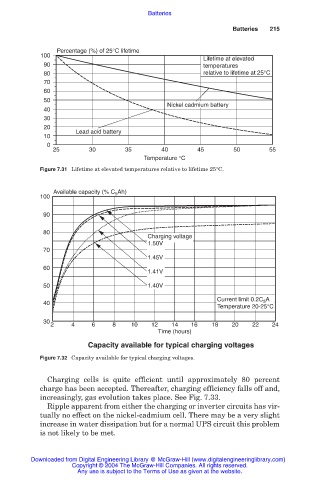
Percentage (%) of 25°C lifetime
100
Lifetime at elevated
90 temperatures
80 relative to lifetime at 25°C
70
60
50
Nickel cadmium battery
40
30
20
Lead acid battery
10
0
25 30 35 40 45 50 55
Temperature °C
Figure 7.31 Lifetime at elevated temperatures relative to lifetime 25°C.
Available capacity (% C Ah)
5
100
90
80
Charging voltage
1.50V
70
1.45V
60
1.41V
50 1.40V
Current limit 0.2C A
40 5
Temperature 20-25°C
30
2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 18 20 22 24
Time (hours)
Capacity available for typical charging voltages
Figure 7.32 Capacity available for typical charging voltages.
Charging cells is quite efficient until approximately 80 percent
charge has been accepted. Thereafter, charging efficiency falls off and,
increasingly, gas evolution takes place. See Fig. 7.33.
Ripple apparent from either the charging or inverter circuits has vir-
tually no effect on the nickel-cadmium cell. There may be a very slight
increase in water dissipation but for a normal UPS circuit this problem
is not likely to be met.
Downloaded from Digital Engineering Library @ McGraw-Hill (www.digitalengineeringlibrary.com)
Copyright © 2004 The McGraw-Hill Companies. All rights reserved.
Any use is subject to the Terms of Use as given at the website.