Page 39 - Using ANSYS for Finite Element Analysis Dynamic, Probabilistic, Design and Heat Transfer Analysis
P. 39
26 • using ansys for finite eLement anaLysis
120
110
100
90
Specific tensile modulus 70
80
60
50
40
30
20
10
0
E-Glass composites S-Glass composites Aramid composites HS carbon composites IM carbon composites
Woods Al.Alloys Titanium Steels
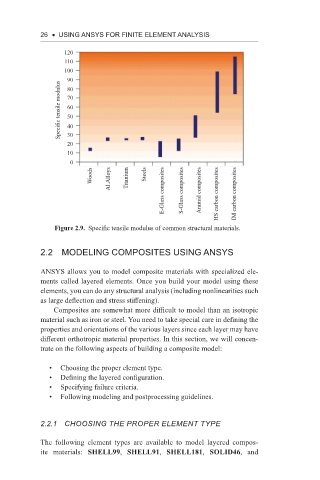
Figure 2.9. Specific tensile modulus of common structural materials.
2.2 modeLing ComPosites using ansys
ANSYS allows you to model composite materials with specialized ele-
ments called layered elements. Once you build your model using these
elements, you can do any structural analysis (including nonlinearities such
as large deflection and stress stiffening).
Composites are somewhat more difficult to model than an isotropic
material such as iron or steel. You need to take special care in defining the
properties and orientations of the various layers since each layer may have
different orthotropic material properties. In this section, we will concen-
trate on the following aspects of building a composite model:
• Choosing the proper element type.
• Defining the layered configuration.
• Specifying failure criteria.
• Following modeling and postprocessing guidelines.
2.2.1 ChooSing The PRoPeR eLeMenT TyPe
The following element types are available to model layered compos-
ite materials: SHELL99, SHELL91, SHELL181, SOLID46, and