Page 324 -
P. 324
UK Government Case Study 7 323
(Department of Health)
NHS
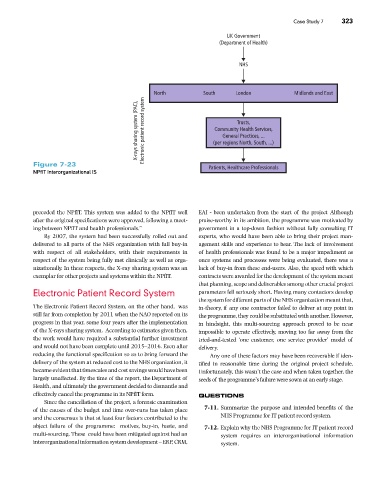
North South London Midlands and East
X-rays sharing system (PAC), Electronic patient record system (per regions North, South, ...)
Trusts,
Community Health Services,
General Practices, ...
Figure 7-23 Patients, Healthcare Professionals
NPfIT Interorganizational IS
preceded the NPfIT. This system was added to the NPfIT well EAI - been undertaken from the start of the project Although
after the original specifications were approved, following a meet- praise-worthy in its ambition, the programme was motivated by
ing between NPfIT and health professionals.” government in a top-down fashion without fully consulting IT
By 2007, the system had been successfully rolled out and experts, who would have been able to bring their project man-
delivered to all parts of the NHS organization with full buy-in agement skills and experience to bear. The lack of involvement
with respect of all stakeholders, with their requirements in of health professionals was found to be a major impediment as
respect of the system being fully met clinically as well as orga- once systems and processes were being evaluated, there was a
nizationally. In these respects, the X-ray sharing system was an lack of buy-in from these end-users. Also, the speed with which
exemplar for other projects and systems within the NPfIT. contracts were awarded for the development of the system meant
that planning, scope and deliverables among other crucial project
Electronic Patient Record System parameters fell seriously short. Having many contactors develop
the system for different parts of the NHS organization meant that,
The Electronic Patient Record System, on the other hand, was in-theory, if any one contractor failed to deliver at any point in
still far from completion by 2011 when the NAO reported on its the programme, they could be substituted with another. However,
progress in that year, some four years after the implementation in hindsight, this multi-sourcing approach proved to be near
of the X-rays sharing system. According to estimates given then, impossible to operate effectively, moving too far away from the
the work would have required a substantial further investment tried-and-tested ‘one customer, one service provider’ model of
and would not have been complete until 2015–2016. Even after delivery.
reducing the functional specification so as to bring forward the Any one of these factors may have been recoverable if iden-
delivery of the system at reduced cost to the NHS organization, it tified in reasonable time during the original project schedule.
became evident that timescales and cost savings would have been Unfortunately, this wasn’t the case and when taken together, the
largely unaffected. By the time of the report, the Department of seeds of the programme’s failure were sown at an early stage.
Health, and ultimately the government decided to dismantle and
effectively cancel the programme in its NPfIT form. QUeStionS
Since the cancellation of the project, a forensic examination
of the causes of the budget and time over-runs has taken place 7-11. Summarize the purpose and intended benefits of the
and the consensus is that at least four factors contributed to the NHS Programme for IT patient record system.
abject failure of the programme: motives, buy-in, haste, and 7-12. Explain why the NHS Programme for IT patient record
multi-sourcing. These could have been mitigated against had an system requires an interorganizational information
interorganizational information system development – ERP, CRM, system.