Page 382 -
P. 382
Q9-3 How Do Organizations Use Data Warehouses and Data Marts to Acquire Data?
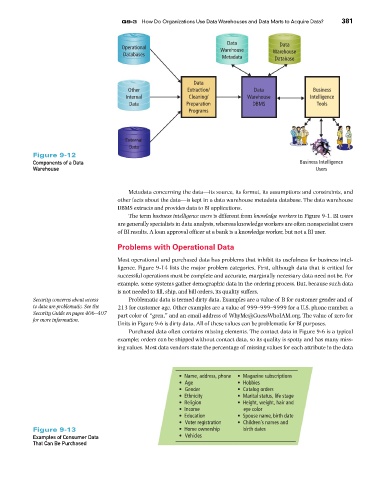
Data Data 381
Operational Warehouse
Databases Metadata Warehouse
Database
Data
Other Extraction/ Data Business
Internal Cleaning/ Warehouse Intelligence
Data Preparation DBMS Tools
Programs
External
Data
Figure 9-12
Components of a Data Business Intelligence
Warehouse Users
Metadata concerning the data—its source, its format, its assumptions and constraints, and
other facts about the data—is kept in a data warehouse metadata database. The data warehouse
DBMS extracts and provides data to BI applications.
The term business intelligence users is different from knowledge workers in Figure 9-1. BI users
are generally specialists in data analysis, whereas knowledge workers are often nonspecialist users
of BI results. A loan approval officer at a bank is a knowledge worker, but not a BI user.
Problems with Operational Data
Most operational and purchased data has problems that inhibit its usefulness for business intel-
ligence. Figure 9-14 lists the major problem categories. First, although data that is critical for
successful operations must be complete and accurate, marginally necessary data need not be. For
example, some systems gather demographic data in the ordering process. But, because such data
is not needed to fill, ship, and bill orders, its quality suffers.
Security concerns about access Problematic data is termed dirty data. Examples are a value of B for customer gender and of
to data are problematic. See the 213 for customer age. Other examples are a value of 999–999–9999 for a U.S. phone number, a
Security Guide on pages 406–407 part color of “gren,” and an email address of WhyMe@GuessWhoIAM.org. The value of zero for
for more information.
Units in Figure 9-6 is dirty data. All of these values can be problematic for BI purposes.
Purchased data often contains missing elements. The contact data in Figure 9-6 is a typical
example; orders can be shipped without contact data, so its quality is spotty and has many miss-
ing values. Most data vendors state the percentage of missing values for each attribute in the data
• Name, address, phone • Magazine subscriptions
• Age • Hobbies
• Gender • Catalog orders
• Ethnicity • Marital status, life stage
• Religion • Height, weight, hair and
• Income eye color
• Education • Spouse name, birth date
• Voter registration • Children‘s names and
Figure 9-13 • Home ownership birth dates
Examples of Consumer Data • Vehicles
That Can Be Purchased