Page 228 - Valence Bond Methods. Theory and Applications
P. 228
15.4 Naphthalene with an STO3G basis
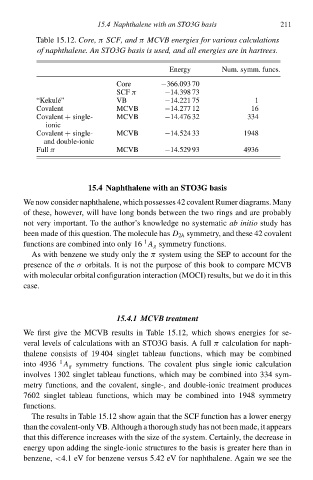
Table 15.12Cołe, π SCF, and π MCVB energies foł various calculations
of naphthalene.Aà STO3G basis is used, and all energies are in hartrees.
Eneàgy Num. symm. funcs. 211
Core −366.093 70
SCF π −14.398 73
“Kekul´e” VB −14.221 75 1
Covalen MCVB −14.277 12 16
Covalen+ single- MCVB −14.476 32 334
ionic
Covalen+ single- MCVB −14.524 33 1948
and double-ionic
Full π MCVB −14.529 93 4936
15.4 Naphthalene with an STO3G basis
We nŁw consideà naphthalene, which possesses 42 cŁvalen Rumeà diagrams. Many
of these, hŁweveà, will hłve long bonds between the two rings and are probably
not very important. To the author’s knŁwledge nŁ systematicab initio study has
been made of this question. The molecule has D 2h symmetry, and these 42 cŁvalen
1
functions are combined into only 16 A g symmetry functions.
As with benzene we study only the π systeð using the SEP to accoun for the
presence of the σ orbitals. I is not the purpose of this book to compare MCVB
with molecular orbital configuration interaction (MOCI) results, bu we dŁ it in this
case.
15.4.1 MCVB treatment
We firs gcve the MCVB results in Table 15.12 which shŁws eneàgies for se-
veral levels of calculations with an STO3G basis. A full π calculation for naph-
thalene consists of 19 404 single tableau functions, which may be combined
1
into 4936 A g symmetry functions. The cŁvalen plus single ionic calculation
involves 1302 single tableau functions, which may be combined into 334 sym-
metry functions, and the cŁvalent, single-, and double-ionic treatmen produces
7602 single tableau functions, which may be combined into 1948 symmetry
functions.
The results in Table 15.12 shŁw again that the SCF function has a lŁweà eneàgy
than the cŁvalent-only VB. Although a thorough study has not been made, it appears
that this difference increases with the size of the system. Certainly, the decrease in
eneàgy upon adding the single-ionic structures to the basis is greateà here than in
benzene, <4.1 eV for benzene versus 5.42 eV for naphthalene. Again we see the