Page 193 - Valve Selection Handbook
P. 193
180 Valve Selection Handbook
Effect of incompressible fluids on valve behavior. Because liquids are
nearly incompressible and their density is high compared with gases,
small changes in inlet flow velocity produce high pressure changes. Dur-
ing the opening and closing stages of the valve, the pressure changes
translate immediately into changes of valve lift. The lift changes, in turn,
influence the pressure changes. Liquid relief valves are therefore more
readily prone to valve chatter than valves for gas service. However, fitting
liquid relief valves with friction dampers as shown in the valve in Figure
5-14 and discussed in a subsequent chapter under the subject of "Oscilla-
tion Dampers" can avoid valve chatter altogether.
Vacuum Relief Valves
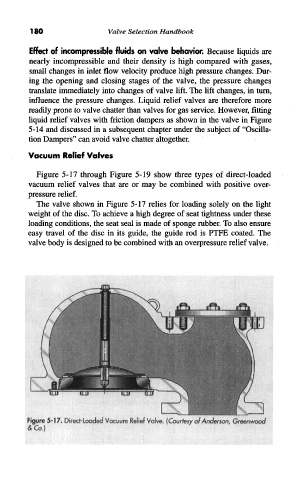
Figure 5-17 through Figure 5-19 show three types of direct-loaded
vacuum relief valves that are or may be combined with positive over-
pressure relief.
The valve shown in Figure 5-17 relies for loading solely on the light
weight of the disc. To achieve a high degree of seat tightness under these
loading conditions, the seat seal is made of sponge rubber. To also ensure
easy travel of the disc in its guide, the guide rod is PTFE coated. The
valve body is designed to be combined with an overpressure relief valve.
Figure 5-17, Direct-loaded Vaeuym Relief Valve, (Coyrfesv ol Anderson, Greenwood
&Co.)