Page 36 - Vibrational Spectroscopic Imaging for Biomedical Applications
P. 36
Towar d Automated Br east Histopathology 13
(a) (b) (c)
0.5 mm
(d) 1.00 (e)1.00
0.99 0.99
AUC 0.98 1.00 AUC 0.98 1.00
0.99
0.99
0.97 0.97
0.98 0.98
0.97 0.97
0.96 0.96 Stroma 0.96 0.96 Stroma
Epithelium Epithelium
0.95 Mean 0.95 Mean
0.95 2 4 6 8 10 0.95 2 4 6 8 10
20 40 60 80 20 40 60 80
Number of metrics Number of metrics
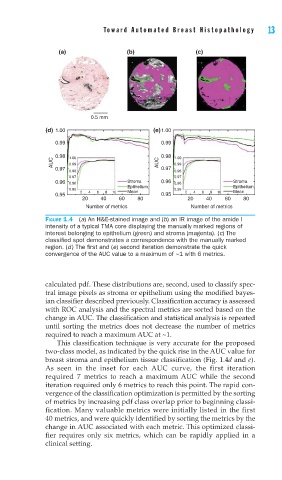
FIGURE 1.4 (a) An H&E-stained image and (b) an IR image of the amide I
intensity of a typical TMA core displaying the manually marked regions of
interest belonging to epithelium (green) and stroma (magenta). (c) The
classifi ed spot demonstrates a correspondence with the manually marked
region. (d) The fi rst and (e) second iteration demonstrate the quick
convergence of the AUC value to a maximum of ~1 with 6 metrics.
calculated pdf. These distributions are, second, used to classify spec-
tral image pixels as stroma or epithelium using the modified bayes-
ian classifier described previously. Classification accuracy is assessed
with ROC analysis and the spectral metrics are sorted based on the
change in AUC. The classification and statistical analysis is repeated
until sorting the metrics does not decrease the number of metrics
required to reach a maximum AUC at ~1.
This classification technique is very accurate for the proposed
two-class model, as indicated by the quick rise in the AUC value for
breast stroma and epithelium tissue classification (Fig. 1.4d and e).
As seen in the inset for each AUC curve, the first iteration
required 7 metrics to reach a maximum AUC while the second
iteration required only 6 metrics to reach this point. The rapid con-
vergence of the classification optimization is permitted by the sorting
of metrics by increasing pdf class overlap prior to beginning classi-
fication. Many valuable metrics were initially listed in the first
40 metrics, and were quickly identified by sorting the metrics by the
change in AUC associated with each metric. This optimized classi-
fier requires only six metrics, which can be rapidly applied in a
clinical setting.