Page 237 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 237
CAT3525_C07.qxd 1/29/2005 9:57 AM Page 208
208 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
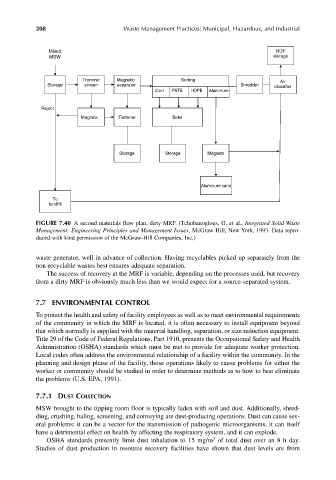
Mixed RDF
MSW storage
Trommel Magnetic Sorting Air
Storage screen separator Shredder
classifier
Corr PETE HDPE Aluminum
Reject
Magnets Flattener Baler
Storage Storage Magnets
Aluminum cans
To
landfill
FIGURE 7.40 A second materials flow plan, dirty MRF. (Tchobanoglous, G. et al., Integrated Solid Waste
Management: Engineering Principles and Management Issues, McGraw Hill, New York, 1993. Data repro-
duced with kind permission of the McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc.)
waste generator, well in advance of collection. Having recyclables picked up separately from the
non-recyclable wastes best ensures adequate separation.
The success of recovery at the MRF is variable, depending on the processes used, but recovery
from a dirty MRF is obviously much less than we would expect for a source-separated system.
7.7 ENVIRONMENTAL CONTROL
To protect the health and safety of facility employees as well as to meet environmental requirements
of the community in which the MRF is located, it is often necessary to install equipment beyond
that which normally is supplied with the material handling, separation, or size reduction equipment.
Title 29 of the Code of Federal Regulations, Part 1910, presents the Occupational Safety and Health
Administration (OSHA) standards which must be met to provide for adequate worker protection.
Local codes often address the environmental relationship of a facility within the community. In the
planning and design phase of the facility, those operations likely to cause problems for either the
worker or community should be studied in order to determine methods as to how to best eliminate
the problems (U.S. EPA, 1991).
7.7.1 DUST COLLECTION
MSW brought to the tipping room floor is typically laden with soil and dust. Additionally, shred-
ding, crushing, baling, screening, and conveying are dust-producing operations. Dust can cause sev-
eral problems: it can be a vector for the transmission of pathogenic microorganisms, it can itself
have a detrimental effect on health by affecting the respiratory system, and it can explode.
3
OSHA standards presently limit dust inhalation to 15 mg/m of total dust over an 8 h day.
Studies of dust production in resource recovery facilities have shown that dust levels are from