Page 258 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 258
CAT3525_C08.qxd 1/29/2005 10:03 AM Page 229
Composting MSW 229
generating about 90 dB at the source. Many states have mandated noise control that limit noise at the
property line. Measures that can reduce noise emanating from the facility include (U.S. EPA, 1994):
● Providing a sufficient buffer zone around the facility with plenty of trees.
● Including noise reduction features in facility design, such as noise hoods, when procur-
ing equipment.
● Properly maintaining mufflers and other equipment components.
● Coordinating hours of operations with adjacent land uses.
● Limiting traffic to and from the facility.
8.8.4 TOXINS WITHIN THE PILE
Many lawns, golf courses, farm fields, and other vegetated areas in the United States receive copi-
ous quantities of herbicides, pesticides, and other biocides. Some have been found to persist after
composting. The ten most commonly used agricultural pesticides in the United States include seven
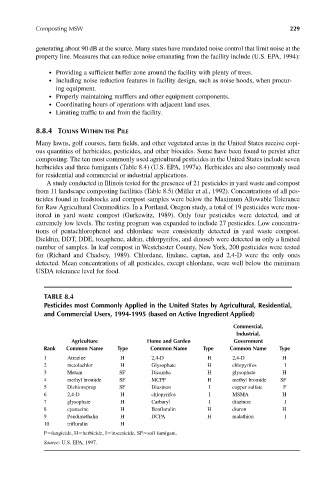
herbicides and three fumigants (Table 8.4) (U.S. EPA, 1997a). Herbicides are also commonly used
for residential and commercial or industrial applications.
A study conducted in Illinois tested for the presence of 21 pesticides in yard waste and compost
from 11 landscape composting facilities (Table 8.5) (Miller et al., 1992). Concentrations of all pes-
ticides found in feedstocks and compost samples were below the Maximum Allowable Tolerance
for Raw Agricultural Commodities. In a Portland, Oregon study, a total of 19 pesticides were mon-
itored in yard waste compost (Gurkewitz, 1989). Only four pesticides were detected, and at
extremely low levels. The testing program was expanded to include 27 pesticides. Low concentra-
tions of pentachlorophenol and chlordane were consistently detected in yard waste compost.
Dieldrin, DDT, DDE, toxaphene, aldrin, chlorpyrifos, and dinoseb were detected in only a limited
number of samples. In leaf compost in Westchester County, New York, 200 pesticides were tested
for (Richard and Chadsey, 1989). Chlordane, lindane, captan, and 2,4-D were the only ones
detected. Mean concentrations of all pesticides, except chlordane, were well below the minimum
USDA tolerance level for food.
TABLE 8.4
Pesticides most Commonly Applied in the United States by Agricultural, Residential,
and Commercial Users, 1994-1995 (based on Active Ingredient Applied)
Commercial,
Industrial,
Agriculture Home and Garden Government
Rank Common Name Type Common Name Type Common Name Type
1 Atrazine H 2,4-D H 2,4-D H
2 metolachlor H Glysophate H chlopyrifos I
3 Metam SF Dicamba H glysophate H
4 methyl bromide SF MCPP H methyl bromide SF
5 Dichloroprop SF Diazinon I copper sulfate F
6 2,4-D H chlopyrifos I MSMA H
7 glysophate H Carbaryl I diazinon I
8 cyanazine H Benfluralin H diuron H
9 Pendimethalin H DCPA H malathion I
10 trifluralin H
F fungicide, H herbicide, I insecticide, SF soil fumigant.
Source: U.S. EPA, 1997.