Page 259 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 259
CAT3525_C08.qxd 1/29/2005 10:03 AM Page 230
230 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
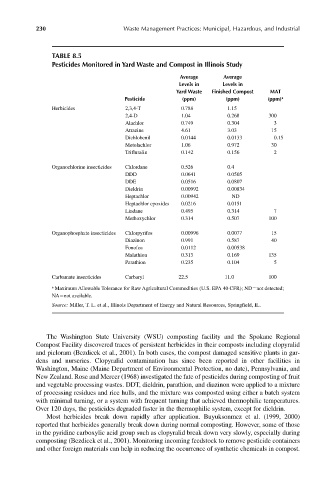
TABLE 8.5
Pesticides Monitored in Yard Waste and Compost in Illinois Study
Average Average
Levels in Levels in
Yard Waste Finished Compost MAT
Pesticide (ppm) (ppm) (ppm) a
Herbicides 2,3,4-T 0.788 1.15
2,4-D 1.04 0.268 300
Alachlor 0.749 0.304 3
Atrazine 4.61 3.03 15
Dichlobenil 0.0144 0.0133 0.15
Metolachlor 1.06 0.972 30
Trifluralin 0.142 0.156 2
Organochlorine insecticides Chlordane 0.526 0.4
DDD 0.0641 0.0505
DDE 0.0516 0.0807
Dieldrin 0.00992 0.00834
Heptachlor 0.00942 ND
Heptachlor epoxides 0.0216 0.0151
Lindane 0.495 0.314 7
Methoxychlor 0.314 0.507 100
Organophosphate insecticides Chlorpyrifos 0.00996 0.0077 15
Diazinon 0.991 0.587 40
Fonofos 0.0112 0.00538
Malathion 0.313 0.169 135
Parathion 0.235 0.104 5
Carbamate insecticides Carbaryl 22.5 11.0 100
a Maximum Allowable Tolerance for Raw Agricultural Commodities (U.S. EPA 40 CFR); ND not detected;
NA not available.
Source: Miller, T. L. et al., Illinois Department of Energy and Natural Resources, Springfield, IL.
The Washington State University (WSU) composting facility and the Spokane Regional
Compost Facility discovered traces of persistent herbicides in their composts including clopyralid
and picloram (Bezdicek et al., 2001). In both cases, the compost damaged sensitive plants in gar-
dens and nurseries. Clopyralid contamination has since been reported in other facilities in
Washington, Maine (Maine Department of Environmental Protection, no date), Pennsylvania, and
New Zealand. Rose and Mercer (1968) investigated the fate of pesticides during composting of fruit
and vegetable processing wastes. DDT, dieldrin, parathion, and diazinon were applied to a mixture
of processing residues and rice hulls, and the mixture was composted using either a batch system
with minimal turning, or a system with frequent turning that achieved thermophilic temperatures.
Over 120 days, the pesticides degraded faster in the thermophilic system, except for dieldrin.
Most herbicides break down rapidly after application. Buyuksonmez et al. (1999, 2000)
reported that herbicides generally break down during normal composting. However, some of those
in the pyridine carboxylic acid group such as clopyralid break down very slowly, especially during
composting (Bezdicek et al., 2001). Monitoring incoming feedstock to remove pesticide containers
and other foreign materials can help in reducing the occurrence of synthetic chemicals in compost.