Page 622 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 622
CAT3525_C20.qxd 1/27/2005 12:54 PM Page 593
Medical and Infectious Wastes 593
The above records must be on hand at the facility for at least 5 years (40 CFR Part 60.58c).
An annual report must be submitted by medical waste incineration facilities for the following data:
● Values for site-specific operating parameters
● The results of any performance tests
● Any use of the bypass stack, the duration, reason for malfunction, and corrective action
taken
20.6 TYPES OF MEDICAL WASTE INCINERATORS
As discussed in Chapter 9, the design function of incineration is to destroy the organic component of
the waste through high-temperature combustion. A secondary function is detoxification of the waste.
The residual ash from incineration may be hazardous as per 40 CFR Part 261 (Identification and Listing
of Hazardous Waste). It must therefore be tested via the TCLP in order to assess possible toxicity.
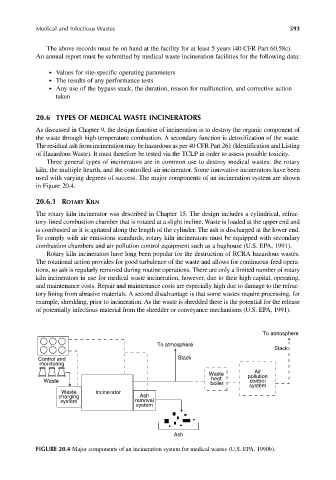
Three general types of incinerators are in common use to destroy medical wastes: the rotary
kiln, the multiple hearth, and the controlled-air incinerator. Some innovative incinerators have been
used with varying degrees of success. The major components of an incineration system are shown
in Figure 20.4.
20.6.1 ROTARY KILN
The rotary kiln incinerator was described in Chapter 15. The design includes a cylindrical, refrac-
tory-lined combustion chamber that is rotated at a slight incline. Waste is loaded at the upper end and
is combusted as it is agitated along the length of the cylinder. The ash is discharged at the lower end.
To comply with air emissions standards, rotary kiln incinerators must be equipped with secondary
combustion chambers and air pollution control equipment such as a baghouse (U.S. EPA, 1991).
Rotary kiln incinerators have long been popular for the destruction of RCRA hazardous wastes.
The rotational action provides for good turbulence of the waste and allows for continuous-feed opera-
tions, so ash is regularly removed during routine operations. There are only a limited number of rotary
kiln incinerators in use for medical waste incineration, however, due to their high capital, operating,
and maintenance costs. Repair and maintenance costs are especially high due to damage to the refrac-
tory lining from abrasive materials. A second disadvantage is that some wastes require processing, for
example, shredding, prior to incineration. As the waste is shredded there is the potential for the release
of potentially infectious material from the shredder or conveyance mechanisms (U.S. EPA, 1991).
To atmosphere
To atmosphere
Stack
Control and Stack
monitoring
Air
Waste
heat pollution
Waste control
boiler
system
Waste Incinerator
charging Ash
system removal
system
Ash
FIGURE 20.4 Major components of an incineration system for medical wastes (U.S. EPA, 1990b).