Page 625 - Materials Chemistry, Second Edition
P. 625
CAT3525_C20.qxd 1/27/2005 12:54 PM Page 596
596 Waste Management Practices: Municipal, Hazardous, and Industrial
Fire door
actuator
Fire door
Primary
Hopper cover combustion
chamber
Waste charging
hopper
Hydraulic Charging
ram actuator
ram
Furnace
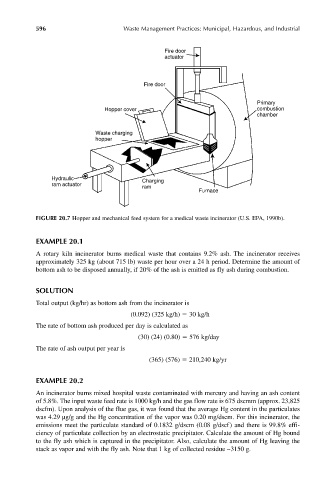
FIGURE 20.7 Hopper and mechanical feed system for a medical waste incinerator (U.S. EPA, 1990b).
EXAMPLE 20.1
A rotary kiln incinerator burns medical waste that contains 9.2% ash. The incinerator receives
approximately 325 kg (about 715 lb) waste per hour over a 24 h period. Determine the amount of
bottom ash to be disposed annually, if 20% of the ash is emitted as fly ash during combustion.
SOLUTION
Total output (kg/hr) as bottom ash from the incinerator is
(0.092) (325 kg/h) 30 kg/h
The rate of bottom ash produced per day is calculated as
(30) (24) (0.80) 576 kg/day
The rate of ash output per year is
(365) (576) 210,240 kg/yr
EXAMPLE 20.2
An incinerator burns mixed hospital waste contaminated with mercury and having an ash content
of 5.8%. The input waste feed rate is 1000 kg/h and the gas flow rate is 675 dscmm (approx. 23,825
dscfm). Upon analysis of the flue gas, it was found that the average Hg content in the particulates
was 4.29 µg/g and the Hg concentration of the vapor was 0.20 mg/dscm. For this incinerator, the
emissions meet the particulate standard of 0.1832 g/dscm (0.08 g/dscf) and there is 99.8% effi-
ciency of particulate collection by an electrostatic precipitator. Calculate the amount of Hg bound
to the fly ash which is captured in the precipitator. Also, calculate the amount of Hg leaving the
stack as vapor and with the fly ash. Note that 1 kg of collected residue ~3150 g.