Page 259 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 259
6-36 WATER AND WASTEWATER ENGINEERING
d. The required input water power can be calculated by using Equation 6-12. Using Table
3
A-1 in Appendix A and the temperature of the water, find 1.519 10 Pa · s.
12 3 3
.
s
6
.
P (600 s ) (1 519 10 Pa
)(0 665 m ) 363 6.or 360 W
Because the efficiency of transfer of motor power to water power is about 80%, the
motor power should be
360 W
Motor power 450 W
08
.
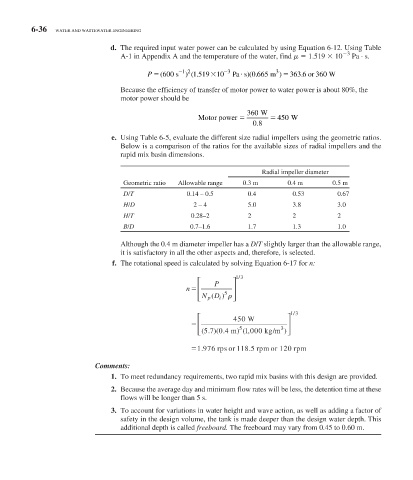
e. Using Table 6-5 , evaluate the different size radial impellers using the geometric ratios.
Below is a comparison of the ratios for the available sizes of radial impellers and the
rapid mix basin dimensions.
Radial impeller diameter
Geometric ratio Allowable range 0.3 m 0.4 m 0.5 m
D/T 0.14 – 0.5 0.4 0.53 0.67
H/D 2 – 4 5.0 3.8 3.0
H/T 0.28–2 2 2 2
B/D 0.7–1.6 1.7 1.3 1.0
Although the 0.4 m diameter impeller has a D / T slightly larger than the allowable range,
it is satisfactory in all the other aspects and, therefore, is selected.
f. The rotational speed is calculated by solving Equation 6-17 for n:
/
⎡ ⎤ 13
n ⎢ P ⎥
5
⎢ ⎣ N D i ) ⎥ ⎦
p (
/
⎡ 450 W ⎤ 13
⎢ ⎥
⎣ ⎢ ( . ) . 5 5 kg/m 3 )⎥ ⎦
57 04 m) 1 000( ,
(
1 976 rps or 118 5 rrpm or 120 rpm
.
.
Comments:
1. To meet redundancy requirements, two rapid mix basins with this design are provided.
2. Because the average day and minimum flow rates will be less, the detention time at these
flows will be longer than 5 s.
3. To account for variations in water height and wave action, as well as adding a factor of
safety in the design volume, the tank is made deeper than the design water depth. This
additional depth is called freeboard. The freeboard may vary from 0.45 to 0.60 m.