Page 262 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 262
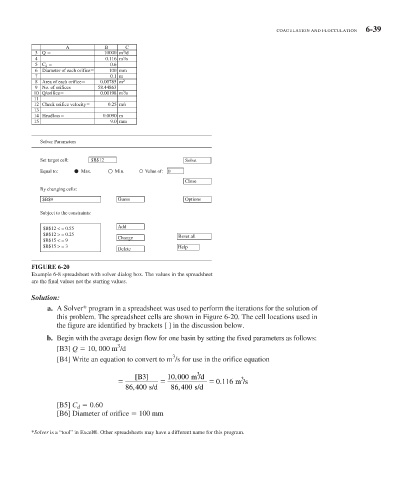
COAGULATION AND FLOCCULATION 6-39
A B C
3 Q 10000 m 3 /d
4 0.116 m 3 /s
5 C d 0.6
6 Diameter of each orifice 100 mm
7 0.1 m
8 Area of each orifice 0.00785 m 2
9 No. of orifices 58.44863
10 Q/orifice 0.00198 m 3 /s
11
12 Check orifice velocity 0.25 m/s
13
14 Headloss 0.0090 m
15 9.0 mm
Solver Parameters
Set target cell: $B$12 Solve
Equal to: Max. Min. Value of: 0
Close
By changing cells:
$B$9 Guess Options
Subject to the constraints:
$B$12 < = 0.55 Add
$B$12 > = 0.25 Reset all
$B$15 < = 9 Change
$B$15 > = 3 Help
Delete
FIGURE 6-20
Example 6-8 spreadsheet with solver dialog box. The values in the spreadsheet
are the final values not the starting values.
Solution:
a. A Solver* program in a spreadsheet was used to perform the iterations for the solution of
this problem. The spreadsheet cells are shown in Figure 6-20 . The cell locations used in
the figure are identified by brackets [ ] in the discussion below.
b. Begin with the average design flow for one basin by setting the fixed parameters as follows:
3
[B3] Q 10, 000 m /d
3
[B4] Write an equation to convert to m /s for use in the orifice equation
3
[B3 ] 10 000 m /d
,
3
0 116 m /s
.
,
,
86 400 s/d 86 400 s/d
[B5] C d 0.60
[B6] Diameter of orifice 100 mm
*Solver is a “tool” in Excel®. Other spreadsheets may have a different name for this program.