Page 494 - Water and wastewater engineering
P. 494
MEMBRANE FILTRATION 12-11
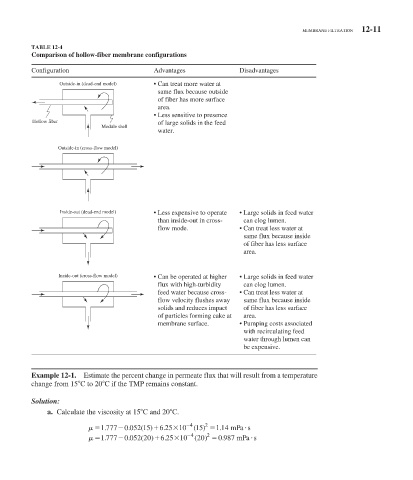
TABLE 12-4
Comparison of hollow-fiber membrane configurations
Configuration Advantages Disadvantages
Outside-in (dead-end model) • Can treat more water at
same flux because outside
of fiber has more surface
area.
• Less sensitive to presence
Hollow fiber of large solids in the feed
Module shell
water.
Outside-in (cross-flow model)
Inside-out (dead-end model) • Less expensive to operate • Large solids in feed water
than inside-out in cross- can clog lumen.
flow mode. • Can treat less water at
same flux because inside
of fiber has less surface
area.
Inside-out (cross-flow model) • Can be operated at higher • Large solids in feed water
flux with high-turbidity can clog lumen.
feed water because cross- • Can treat less water at
flow velocity flushes away same flux because inside
solids and reduces impact of fiber has less surface
of particles forming cake at area.
membrane surface. • Pumping costs associated
with recirculating feed
water through lumen can
be expensive.
Example 12-1. Estimate the percent change in permeate flux that will result from a temperature
change from 15 C to 20 C if the TMP remains constant.
Solution:
a. Calculate the viscosity at 15 C and 20 C.
4
1 777 0 052 15() 6 25 10 () 2 1 14 mPa s
.
.
.
.
15
4 2
1 777. 0 052 20. ( ) 6 25. 10 ( 20) 0 987. mPa s