Page 120 - Welding Robots Technology, System Issues, and Applications
P. 120
Robotic Welding: System Issues 107
welding parameters are the voltage, the wire feed rate, and the torch
speed. Technically, the voltage and the wire feed rate are analog signals
commanded to the welding power source, and generated from the robot
controller or process PLC. The torch speed is the desired speed
commanded to the robot TCP for coordinated motion.
2. Secondary inputs: variables defined when the process is selected and
before any welding service. Using again as example the GMAW process
those parameters include the type or composition of the shielding gas, the
flow of gas during the process, the torch angle, and the type and size of
the wire to use.
3. Fixed inputs: parameters that are fixed and cannot be changed by the
user. These parameters are usually an imposition of the selected welding
process, of the current welding procedure or of the physical setup.
Parameters of this type include the joint geometry, plate thickness,
physical properties of the plate metal, etc.
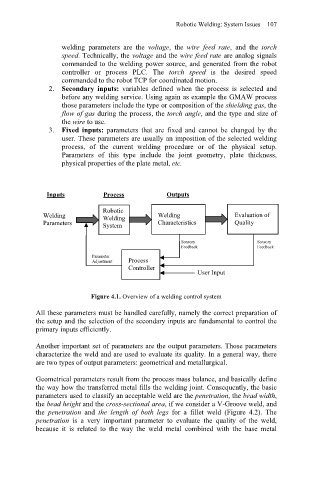
Inputs Process Outputs
Robotic
Welding Welding Welding Evaluation of
Parameters System Characteristics Quality
Sensory Sensory
Feedback Feedback
Parameter
Adjustment Process
Controller
User Input
Figure 4.1. Overview of a welding control system
All these parameters must be handled carefully, namely the correct preparation of
the setup and the selection of the secondary inputs are fundamental to control the
primary inputs efficiently.
Another important set of parameters are the output parameters. Those parameters
characterize the weld and are used to evaluate its quality. In a general way, there
are two types of output parameters: geometrical and metallurgical.
Geometrical parameters result from the process mass balance, and basically define
the way how the transferred metal fills the welding joint. Consequently, the basic
parameters used to classify an acceptable weld are the penetration, the bead width,
the bead height and the cross-sectional area, if we consider a V-Groove weld, and
the penetration and the length of both legs for a fillet weld (Figure 4.2). The
penetration is a very important parameter to evaluate the quality of the weld,
because it is related to the way the weld metal combined with the base metal