Page 74 - Fluid Power Engineering
P. 74
52 Chapter Four
where ρ is the density and v 0 is the free stream wind speed. If there
is no circulation, there is no lift. What is circulation? Mathematically,
circulation around a body is defined as the sum of velocity along a
closed path.
→ →
= v . d s (4-20)
where the closed path is around the object that is subject to lift. The in-
tegral sums the dot product of the velocity along the path. The circula-
tion around any closed path around a cylinder spinning with angular
speed ω is:
= ω2πR 2 (4-21)
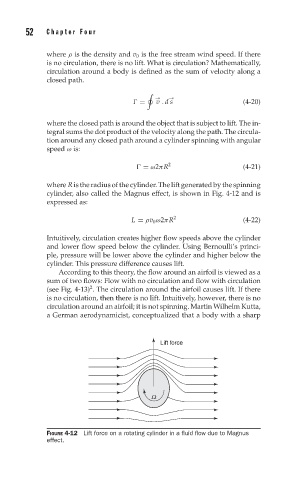
where R is the radius of the cylinder. The lift generated by the spinning
cylinder, also called the Magnus effect, is shown in Fig. 4-12 and is
expressed as:
L = ρv 0 ω2πR 2 (4-22)
Intuitively, circulation creates higher flow speeds above the cylinder
and lower flow speed below the cylinder. Using Bernoulli’s princi-
ple, pressure will be lower above the cylinder and higher below the
cylinder. This pressure difference causes lift.
According to this theory, the flow around an airfoil is viewed as a
sum of two flows: Flow with no circulation and flow with circulation
2
(see Fig. 4-13) . The circulation around the airfoil causes lift. If there
is no circulation, then there is no lift. Intuitively, however, there is no
circulation around an airfoil; it is not spinning. Martin Wilhelm Kutta,
a German aerodynamicist, conceptualized that a body with a sharp
Lift force
W
FIGURE 4-12 Lift force on a rotating cylinder in a fluid flow due to Magnus
effect.