Page 173 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 173
150 Cha pte r F i v e
structure, however, gross void formation has been found, and it was
postulated that such voids may result from Al removal in the form of
volatile halides [5-32]. The activation energy for mechanical bond fail-
ure due to brominated epoxies was found to be 0.8 eV. Others [5-33],
however, found much lower activation energies for resistive bond fail-
ure (as opposed to mechanical) ranging from 0.2 to 0.5 eV. Thomas
applied the brominated resin directly to the bond areas. He also gave
a chain of chemical reactions that can lead to the resistive bond fail-
ures. The conclusions were that most of the reaction occurred with
free bromine ions and that if the resins were purified of them, then
failures, while not eliminated, would be significantly reduced.
Still other studies of ball-bond degradation from outgassed prod-
ucts of die-attach epoxies in hermetic packages caused ball-bond
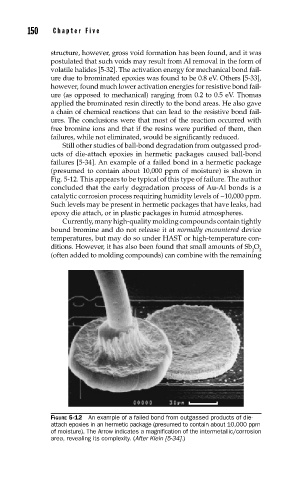
failures [5-34]. An example of a failed bond in a hermetic package
(presumed to contain about 10,000 ppm of moisture) is shown in
Fig. 5-12. This appears to be typical of this type of failure. The author
concluded that the early degradation process of Au-Al bonds is a
catalytic corrosion process requiring humidity levels of ~10,000 ppm.
Such levels may be present in hermetic packages that have leaks, had
epoxy die attach, or in plastic packages in humid atmospheres.
Currently, many high-quality molding compounds contain tightly
bound bromine and do not release it at normally encountered device
temperatures, but may do so under HAST or high-temperature con-
ditions. However, it has also been found that small amounts of Sb O
2 3
(often added to molding compounds) can combine with the remaining
FIGURE 5-12 An example of a failed bond from outgassed products of die-
attach epoxies in an hermetic package (presumed to contain about 10,000 ppm
of moisture). The Arrow indicates a magnifi cation of the intermetallic/corrosion
area, revealing its complexity. (After Klein [5-34].)