Page 28 - Wire Bonding in Microelectronics
P. 28
The Technical Intr oduction to the Thir d Edition 7
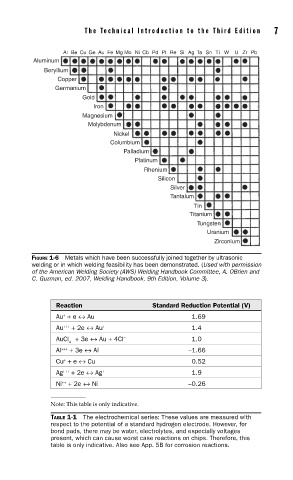
Al Be Cu Ge Au Fe Mg Mo Ni Cb Pd Pt Re Si Ag Ta Sn Ti W U Zr Pb
Aluminum
Beryllium
Copper
Germanium
Gold
Iron
Magnesium
Molybdenum
Nickel
Columbium
Palladium
Platinum
Rhenium
Silicon
Silver
Tantalum
Tin
Titanium
Tungsten
Uranium
Zirconium
FIGURE 1-6 Metals which have been successfully joined together by ultrasonic
welding or in which welding feasibility has been demonstrated. (Used with permission
of the American Welding Society (AWS) Welding Handbook Committee, A. OBrien and
C. Guzman, ed. 2007, Welding Handbook, 9th Edition, Volume 3).
Reaction Standard Reduction Potential (V)
+
Au + e ↔ Au 1.69
Au +++ + 2e ↔ Au + 1.4
−
AuCl + 3e ↔ Au + 4Cl − 1.0
4
Al +++ + 3e ↔ Al −1.66
+
Cu + e ↔ Cu 0.52
Ag +++ + 2e ↔ Ag + 1.9
++
Ni + 2e ↔ Ni −0.26
Note: This table is only indicative.
TABLE 1-1 The electrochemical series: These values are measured with
respect to the potential of a standard hydrogen electrode. However, for
bond pads, there may be water, electrolytes, and especially voltages
present, which can cause worst case reactions on chips. Therefore, this
table is only indicative. Also see App. 5B for corrosion reactions.