Page 147 - Petroleum Production Engineering, A Computer-Assisted Approach
P. 147
Guo, Boyun / Computer Assited Petroleum Production Engg 0750682701_chap11 Final Proof page 142 3.1.2007 8:54pm Compositor Name: SJoearun
11/142 EQUIPMENT DESIGN AND SELECTION
40
Aspirated Input Motor
Turbocharged Input Motor
Percent Reduction in Input Horsepower 20
30
10
0
0 2 4 6 8 10
Surface Location Elevation (1,000 ft)
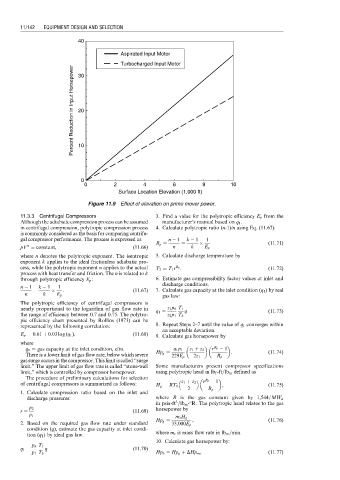
Figure 11.9 Effect of elevation on prime mover power.
11.3.3 Centrifugal Compressors 3. Find a value for the polytropic efficiency E p from the
Although the adiabatic compression process can be assumed manufacturer’s manual based on q 1 .
in centrifugal compression, polytropic compression process 4. Calculate polytropic ratio (n-1)/n using Eq. (11.67):
is commonly considered as the basis for comparing centrifu-
gal compressor performance. The process is expressed as n 1 k 1 1
R p ¼ ¼ (11:71)
n
pV ¼ constant, (11:66) n k E p
where n denotes the polytropic exponent. The isentropic 5. Calculate discharge temperature by
exponent k applies to the ideal frictionless adiabatic pro-
cess, while the polytropic exponent n applies to the actual T 2 ¼ T 1 r : (11:72)
R p
process with heat transfer and friction. The n is related to k
through polytropic efficiency E p : 6. Estimate gas compressibility factor values at inlet and
discharge conditions.
n 1 k 1 1
¼ : (11:67) 7. Calculate gas capacity at the inlet condition (q 1 ) by real
n k E p gas law:
The polytropic efficiency of centrifugal compressors is
nearly proportional to the logarithm of gas flow rate in q 1 ¼ z 1 p b T 1 q (11:73)
the range of efficiency between 0.7 and 0.75. The polytro- z 2 p 1 T b
pic efficiency chart presented by Rollins (1973) can be
represented by the following correlation: 8. Repeat Steps 2–7 until the value of q 1 converges within
an acceptable deviation.
E p ¼ 0:61 þ 0:03 log (q 1 ), (11:68) 9. Calculate gas horsepower by
where
q 1 ¼ gas capacity at the inlet condition, cfm. q 1 p 1 z 1 þ z 2 r R p 1
There is a lower limit of gas flow rate, below which severe Hp g ¼ 229E p 2z 1 R p : (11:74)
gas surge occurs in the compressor. This limit is called ‘‘surge
limit.’’ The upper limit of gas flow rate is called ‘‘stone-wall Some manufacturers present compressor specifications
limit,’’ which is controlled by compressor horsepower. using polytropic head in lb f -ft=lb m defined as
The procedure of preliminary calculations for selection R p
of centrifugal compressors is summarized as follows: z 1 þ z 2 r 1 , (11:75)
H g ¼ RT 1
2 R p
1. Calculate compression ratio based on the inlet and
discharge pressures: where R is the gas constant given by 1,544=MW a
3
in psia-ft =lb m - R. The polytropic head relates to the gas
p 2 horsepower by
r ¼ (11:69)
p 1
m t H g
Hp g ¼ , (11:76)
2. Based on the required gas flow rate under standard 33,000E p
condition (q), estimate the gas capacity at inlet condi-
tion (q 1 ) by ideal gas law: where m t is mass flow rate in lb m =min.
10. Calculate gas horsepower by:
p b T 1
q 1 ¼ q (11:70)
p 1 T b Hp b ¼ Hp g þ DHp m , (11:77)