Page 239 - Petroleum Production Engineering, A Computer-Assisted Approach
P. 239
Guo, Boyun / Computer Assited Petroleum Production Engg 0750682701_chap15 Final Proof page 237 22.12.2006 6:14pm
WELL PROBLEM IDENTIFICATION 15/237
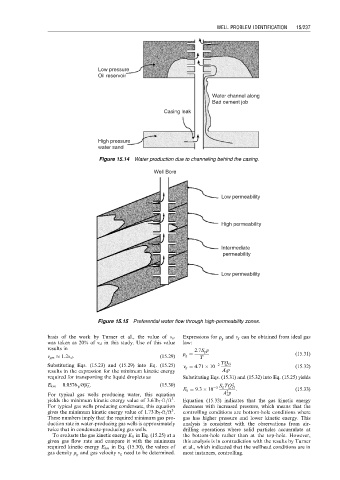
Low pressure
Oil reservoir
Water channel along
Bad cement job
Casing leak
High pressure
water sand
Figure 15.14 Water production due to channeling behind the casing.
Well Bore
Low permeability
High permeability
Intermediate
permeability
Low permeability
Figure 15.15 Preferential water flow through high-permeability zones.
Expressions for r g and v g can be obtained from ideal gas
basis of the work by Turner et al., the value of v tr
was taken as 20% of v sl in this study. Use of this value law:
results in 2:7S g p
r g ¼ (15:31)
v gm 1:2v sl : (15:29) T
Substituting Eqs. (15.23) and (15.29) into Eq. (15.25) v g ¼ 4:71 10 2 TQ G (15:32)
results in the expression for the minimum kinetic energy A i p
required for transporting the liquid droplets as Substituting Eqs. (15.31) and (15.32) into Eq. (15.25) yields
p ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
E km ¼ 0:0576 sr L : (15:30) S g TQ 2
E k ¼ 9:3 10 5 2 G : (15:33)
For typical gas wells producing water, this equation A p
i
3
yields the minimum kinetic energy value of 3:6lb f -ft=ft . Equation (15.33) indicates that the gas kinetic energy
For typical gas wells producing condensate, this equation decreases with increased pressure, which means that the
3
gives the minimum kinetic energy value of 1:73 lb f -ft=ft . controlling conditions are bottom-hole conditions where
These numbers imply that the required minimum gas pro- gas has higher pressure and lower kinetic energy. This
duction rate in water-producing gas wells is approximately analysis is consistent with the observations from air-
twice that in condensate-producing gas wells. drilling operations where solid particles accumulate at
To evaluate the gas kinetic energy E k in Eq. (15.25) at a the bottom-hole rather than at the top-hole. However,
given gas flow rate and compare it with the minimum this analysis is in contradiction with the results by Turner
required kinetic energy E km in Eq. (15.30), the values of et al., which indicated that the wellhead conditions are in
gas density r g and gas velocity v g need to be determined. most instances, controlling.