Page 70 - Petroleum Production Engineering, A Computer-Assisted Approach
P. 70
Guo, Boyun / Petroleum Production Engineering, A Computer-Assisted Approach 0750682701_chap05 Final Proof page 61 21.12.2006 2:02pm
CHOKE PERFORMANCE 5/61
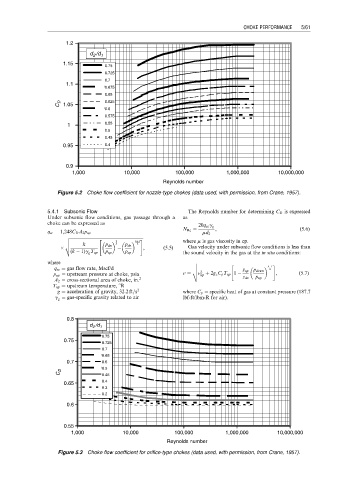
1.2
d /d 1
2
1.15
0.75
0.725
0.7
1.1
0.675
0.65
C D 1.05 0.625
0.6
0.575
1 0.55
0.5
0.45
0.95 0.4
0.9
1,000 10,000 100,000 1,000,000 10,000,000
Reynolds number
Figure 5.2 Choke flow coefficient for nozzle-type chokes (data used, with permission, from Crane, 1957).
5.4.1 Subsonic Flow The Reynolds number for determining C D is expressed
Under subsonic flow conditions, gas passage through a as
choke can be expressed as
20q sc g g
N Re ¼ , (5:6)
q sc ¼ 1,248C D A 2 p up md 2
v ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi
u " 2 # where m is gas viscosity in cp.
u k k kþ1 k
t p dn p dn , (5:5) Gas velocity under subsonic flow conditions is less than
(k 1)g g T up p up p up the sound velocity in the gas at the in situ conditions:
where v ffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffiffi #
"
u
q sc ¼ gas flow rate, Mscf/d u z up p down k 1
k
p up ¼ upstream pressure at choke, psia n ¼ t n 2 up þ 2g c C p T up 1 , (5:7)
A 2 ¼ cross-sectional area of choke, in: 2 z dn p up
T up ¼ upstream temperature, 8R
g ¼ acceleration of gravity, 32:2ft=s 2 where C p ¼ specific heat of gas at constant pressure (187.7
g g ¼ gas-specific gravity related to air lbf-ft/lbm-R for air).
0.8
d /d 1
2
0.75
0.75
0.725
0.7
0.65
0.7 0.6
0.5
C D 0.45
0.65 0.4
0.3
0.2
0.6
0.55
1,000 10,000 100,000 1,000,000 10,000,000
Reynolds number
Figure 5.3 Choke flow coefficient for orifice-type chokes (data used, with permission, from Crane, 1957).