Page 128 - 3D Fibre Reinforced Polymer Composites
P. 128
30 Woven Composites 117
bearing tows, which may have been significantly weakened by damage incurred in the
3D weaving process (see Figure 5.3). As a result, the tensile strength of a 3D woven
composite is often lower than for an equivalent 2D woven composite with a similar
fibre volume content (Brandt et al., 1996; Cox and Flanagan, 1996; Lee et al., 1992).
Figure 5.11 presents a compilation of published tensile strength data for 3D woven
composites with different z-binder contents. In this figure the tensile strength of a 3D
woven composite is normalised to the strength of the equivalent 2D laminate. It is seen
that the failure strength of 3D woven composites is the same or, more often, less than
the strength of the 2D laminate. It is interesting to note, however, that the tensile
strength of a 3D composite is rarely more than 20% lower than the strength of the 2D
material, and furthermore the tensile strength is not affected significantly by the z-
binder content for the range plotted here. The lower tensile strength of 3D woven
composites is due to fibre damage incurred during the weaving process that weakens the
low-bearing tows (see Figure 5.3), increased fibre waviness, and pinching of the surface
tows (see Figure 5.4).
1600 '800F
l0O0t I
20 Woven Laminate
600
3D Woven Composite
200
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Fibre Waviness (degrees)
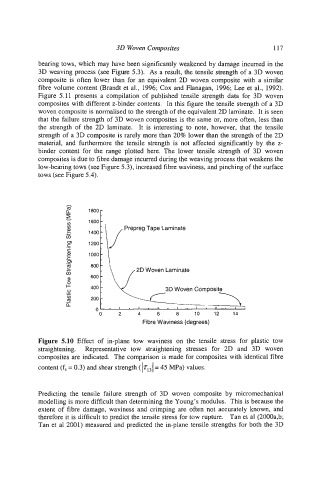
Figure 5.10 Effect of in-plane tow waviness on the tensile stress for plastic tow
straightening. Representative tow straightening stresses for 2D and 3D woven
composites are indicated. The comparison is made for composites with identical fibre
content (f, = 0.3) and shear strength ( 1T131 = 45 MPa) values.
Predicting the tensile failure strength of 3D woven composite by micromechanical
modelling is more difficult than determining the Young's modulus. This is because the
extent of fibre damage, waviness and crimping are often not accurately known, and
therefore it is difficult to predict the tensile stress for tow rupture. Tan et a1 (2000a,b;
Tan et a1 2001) measured and predicted the in-plane tensile strengths for both the 3D