Page 204 -
P. 204
6 - PROJECT TIME MANAGEMENT
6.6.2.3 critical chain Method
The critical chain method (CCM) is a schedule method that allows the project team to place buffers on any
project schedule path to account for limited resources and project uncertainties. It is developed from the critical
path method approach and considers the effects of resource allocation, resource optimization, resource leveling,
and activity duration uncertainty on the critical path determined using the critical path method. To do so, the critical
chain method introduces the concept of buffers and buffer management. The critical chain method uses activities
with durations that do not include safety margins, logical relationships, and resource availability with statistically
determined buffers composed of the aggregated safety margins of activities at specified points on the project
schedule path to account for limited resources and project uncertainties. The resource-constrained critical path is
known as the critical chain.
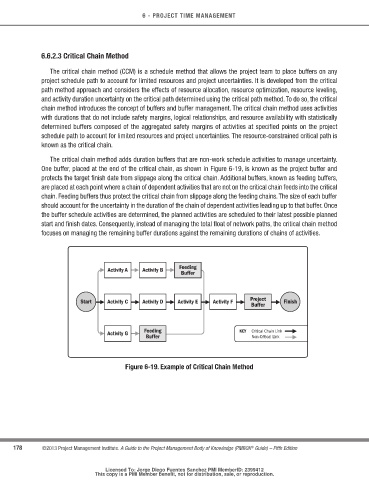
The critical chain method adds duration buffers that are non-work schedule activities to manage uncertainty.
One buffer, placed at the end of the critical chain, as shown in Figure 6-19, is known as the project buffer and
protects the target finish date from slippage along the critical chain. Additional buffers, known as feeding buffers,
are placed at each point where a chain of dependent activities that are not on the critical chain feeds into the critical
chain. Feeding buffers thus protect the critical chain from slippage along the feeding chains. The size of each buffer
should account for the uncertainty in the duration of the chain of dependent activities leading up to that buffer. Once
the buffer schedule activities are determined, the planned activities are scheduled to their latest possible planned
start and finish dates. Consequently, instead of managing the total float of network paths, the critical chain method
focuses on managing the remaining buffer durations against the remaining durations of chains of activities.
Feeding
Activity A Activity B
Buffer
Start Activity C Activity D Activity E Activity F Project Finish
Buffer
Activity G Feeding KEY Critical Chain Link
Buffer Non-Critical Link
Figure 6-19. Example of critical chain Method
178 ©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition
®
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.