Page 248 -
P. 248
7 - PROJECT COST MANAGEMENT
Status Date
TCPI
>1 (BAC)
1.00 Baseline Plan
TCPI
(EAC)
<1
Cumulative
CPI
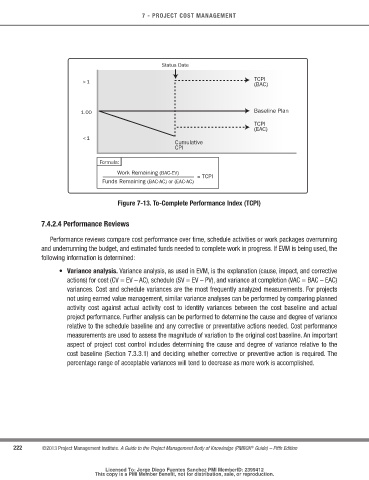
Formula:
Work Remaining (BAC-EV)
= TCPI
Funds Remaining (BAC-AC) or (EAC-AC)
Figure 7-13. to-complete Performance Index (tcPI)
7.4.2.4 Performance reviews
Performance reviews compare cost performance over time, schedule activities or work packages overrunning
and underrunning the budget, and estimated funds needed to complete work in progress. If EVM is being used, the
following information is determined:
• Variance analysis. Variance analysis, as used in EVM, is the explanation (cause, impact, and corrective
actions) for cost (CV = EV – AC), schedule (SV = EV – PV), and variance at completion (VAC = BAC – EAC)
variances. Cost and schedule variances are the most frequently analyzed measurements. For projects
not using earned value management, similar variance analyses can be performed by comparing planned
activity cost against actual activity cost to identify variances between the cost baseline and actual
project performance. Further analysis can be performed to determine the cause and degree of variance
relative to the schedule baseline and any corrective or preventative actions needed. Cost performance
measurements are used to assess the magnitude of variation to the original cost baseline. An important
aspect of project cost control includes determining the cause and degree of variance relative to the
cost baseline (Section 7.3.3.1) and deciding whether corrective or preventive action is required. The
percentage range of acceptable variances will tend to decrease as more work is accomplished.
222 ©2013 Project Management Institute. A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK Guide) – Fifth Edition
®
Licensed To: Jorge Diego Fuentes Sanchez PMI MemberID: 2399412
This copy is a PMI Member benefit, not for distribution, sale, or reproduction.