Page 122 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 122
2.5 DATA ACQUISITION PARAMETERS 113
followingagentsshouldbeconsidered,whichare • Maximum and dominant frequency at the
generally obtained from 2D vintage seismic data: target level
• HSE regulations for the survey and working
• Depth, size, type and other characteristics of environment
the target
• Maximum expected subsurface dip The acquisition parameters that should be
• Depths ofshallowest anddeepesttarget levels predetermined before the survey can be classi-
• Two-way arrival time of target reflections fied into two groups:
• Appropriate fold for a high-quality dataset
(i) Acquisition parameters directly related to
• V RMS distribution down to the deepest
the seismic spread geometry, and some
target level
specific characteristics of sources and
• Desired temporal and spatial resolution
receivers (Table 2.3). The nominal offsets
• Specific noise types, if exist
and general geometrical parameters for 2D
• Area for a complete image
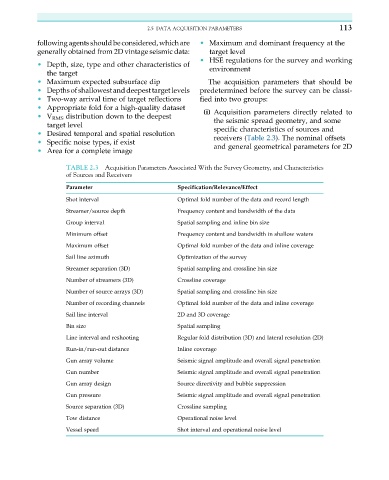
TABLE 2.3 Acquisition Parameters Associated With the Survey Geometry, and Characteristics
of Sources and Receivers
Parameter Specification/Relevance/Effect
Shot interval Optimal fold number of the data and record length
Streamer/source depth Frequency content and bandwidth of the data
Group interval Spatial sampling and inline bin size
Minimum offset Frequency content and bandwidth in shallow waters
Maximum offset Optimal fold number of the data and inline coverage
Sail line azimuth Optimization of the survey
Streamer separation (3D) Spatial sampling and crossline bin size
Number of streamers (3D) Crossline coverage
Number of source arrays (3D) Spatial sampling and crossline bin size
Number of recording channels Optimal fold number of the data and inline coverage
Sail line interval 2D and 3D coverage
Bin size Spatial sampling
Line interval and reshooting Regular fold distribution (3D) and lateral resolution (2D)
Run-in/run-out distance Inline coverage
Gun array volume Seismic signal amplitude and overall signal penetration
Gun number Seismic signal amplitude and overall signal penetration
Gun array design Source directivity and bubble suppression
Gun pressure Seismic signal amplitude and overall signal penetration
Source separation (3D) Crossline sampling
Tow distance Operational noise level
Vessel speed Shot interval and operational noise level