Page 160 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 160
2.6 QC IN DATA ACQUISITION 151
attached to the streamers. They cooperate with reference position. Reliable operation of the
the acoustic ranging to maintain the nominal rGPS system during the entire survey is critical
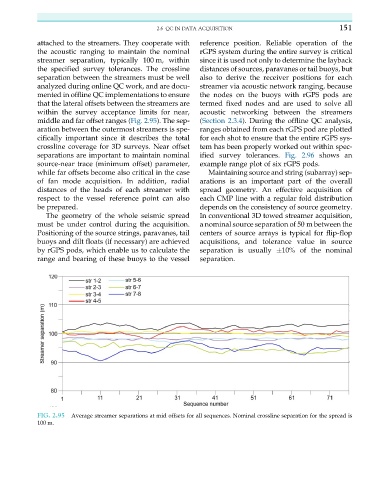
streamer separation, typically 100 m, within since it is used not only to determine the layback
the specified survey tolerances. The crossline distances of sources, paravanes or tail buoys, but
separation between the streamers must be well also to derive the receiver positions for each
analyzed during online QC work, and are docu- streamer via acoustic network ranging, because
mented in offline QC implementations to ensure the nodes on the buoys with rGPS pods are
that the lateral offsets between the streamers are termed fixed nodes and are used to solve all
within the survey acceptance limits for near, acoustic networking between the streamers
middle and far offset ranges (Fig. 2.95). The sep- (Section 2.3.4). During the offline QC analysis,
aration between the outermost streamers is spe- ranges obtained from each rGPS pod are plotted
cifically important since it describes the total for each shot to ensure that the entire rGPS sys-
crossline coverage for 3D surveys. Near offset tem has been properly worked out within spec-
separations are important to maintain nominal ified survey tolerances. Fig. 2.96 shows an
source-near trace (minimum offset) parameter, example range plot of six rGPS pods.
while far offsets become also critical in the case Maintaining source and string (subarray) sep-
of fan mode acquisition. In addition, radial arations is an important part of the overall
distances of the heads of each streamer with spread geometry. An effective acquisition of
respect to the vessel reference point can also each CMP line with a regular fold distribution
be prepared. depends on the consistency of source geometry.
The geometry of the whole seismic spread In conventional 3D towed streamer acquisition,
must be under control during the acquisition. a nominal source separation of 50 m between the
Positioning of the source strings, paravanes, tail centers of source arrays is typical for flip-flop
buoys and dilt floats (if necessary) are achieved acquisitions, and tolerance value in source
by rGPS pods, which enable us to calculate the separation is usually 10% of the nominal
range and bearing of these buoys to the vessel separation.
FIG. 2.95 Average streamer separations at mid offsets for all sequences. Nominal crossline separation for the spread is
100 m.