Page 236 - Acquisition and Processing of Marine Seismic Data
P. 236
4.6 2D FOURIER TRANSFORM 227
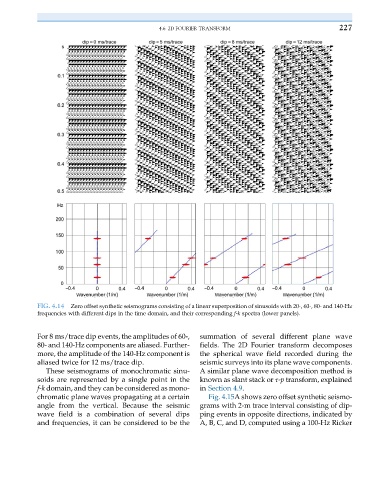
FIG. 4.14 Zero offset synthetic seismograms consisting of a linear superposition of sinusoids with 20-, 60-, 80- and 140-Hz
frequencies with different dips in the time domain, and their corresponding f-k spectra (lower panels).
For 8 ms/trace dip events, the amplitudes of 60-, summation of several different plane wave
80- and 140-Hz components are aliased. Further- fields. The 2D Fourier transform decomposes
more, the amplitude of the 140-Hz component is the spherical wave field recorded during the
aliased twice for 12 ms/trace dip. seismic surveys into its plane wave components.
These seismograms of monochromatic sinu- A similar plane wave decomposition method is
soids are represented by a single point in the known as slant stack or τ-p transform, explained
f-k domain, and they can be considered as mono- in Section 4.9.
chromatic plane waves propagating at a certain Fig. 4.15A shows zero offset synthetic seismo-
angle from the vertical. Because the seismic grams with 2-m trace interval consisting of dip-
wave field is a combination of several dips ping events in opposite directions, indicated by
and frequencies, it can be considered to be the A, B, C, and D, computed using a 100-Hz Ricker