Page 118 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 118
ADSORPTION FROM SOLUTION AND EFFECTS OF SURFACE FUNCTIONALITIES 103
◦
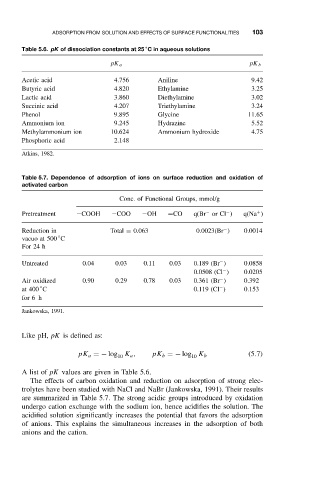
Table 5.6. pK of dissociation constants at 25 C in aqueous solutions
pK a pK b
Acetic acid 4.756 Aniline 9.42
Butyric acid 4.820 Ethylamine 3.25
Lactic acid 3.860 Diethylamine 3.02
Succinic acid 4.207 Triethylamine 3.24
Phenol 9.895 Glycine 11.65
Ammonium ion 9.245 Hydrazine 5.52
Methylammonium ion 10.624 Ammonium hydroxide 4.75
Phosphoric acid 2.148
Atkins, 1982.
Table 5.7. Dependence of adsorption of ions on surface reduction and oxidation of
activated carbon
Conc. of Functional Groups, mmol/g
−
+
−
Pretreatment −COOH −COO −OH =CO q(Br or Cl ) q(Na )
−
Reduction in Total = 0.063 0.0023(Br ) 0.0014
◦
vacuo at 500 C
For 24 h
Untreated 0.04 0.03 0.11 0.03 0.189 (Br ) 0.0858
−
0.0508 (Cl ) 0.0205
−
Air oxidized 0.90 0.29 0.78 0.03 0.361 (Br ) 0.392
−
◦
at 400 C 0.119 (Cl ) 0.153
−
for 6 h
Jankowska, 1991.
Like pH, pK is defined as:
pK a =− log K a , pK b =− log K b (5.7)
10
10
A list of pK values are given in Table 5.6.
The effects of carbon oxidation and reduction on adsorption of strong elec-
trolytes have been studied with NaCl and NaBr (Jankowska, 1991). Their results
are summarized in Table 5.7. The strong acidic groups introduced by oxidation
undergo cation exchange with the sodium ion, hence acidifies the solution. The
acidified solution significantly increases the potential that favors the adsorption
of anions. This explains the simultaneous increases in the adsorption of both
anions and the cation.