Page 131 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 131
116 ACTIVATED CARBON
In kinetic separation, both equilibrium amount and diffusion rates are impor-
tant. A sorbent selection parameter (S k ) has been given in Chapter 3. It involves
both diffusivity and equilibrium constant. The equilibrium isotherms and diffusion
time constants for a number of important sorbates on CMS’s are given below.
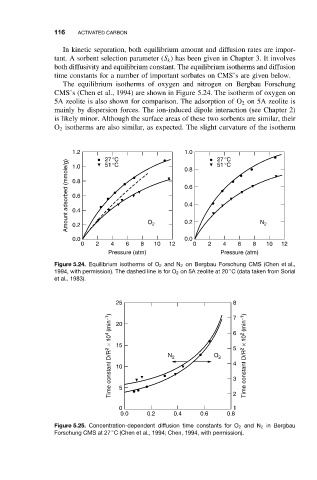
The equilibrium isotherms of oxygen and nitrogen on Bergbau Forschung
CMS’s (Chen et al., 1994) are shown in Figure 5.24. The isotherm of oxygen on
5A zeolite is also shown for comparison. The adsorption of O 2 on 5A zeolite is
mainly by dispersion forces. The ion-induced dipole interaction (see Chapter 2)
is likely minor. Although the surface areas of these two sorbents are similar, their
O 2 isotherms are also similar, as expected. The slight curvature of the isotherm
1.2 27°C 1.0 27°C
Amount adsorbed (mmole/g) 0.8 0.6
51°C
51°C
1.0
0.8
0.6
0.4
0.4
0.2
0.0 O 2 0.2 N 2
0.0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 0 2 4 6 8 10 12
Pressure (atm) Pressure (atm)
Figure 5.24. Equilibrium isotherms of O 2 and N 2 on Bergbau Forschung CMS (Chen et al.,
◦
1994, with permission). The dashed line is for O 2 on 5A zeolite at 20 C (data taken from Sorial
et al., 1983).
25 8
× 10 4 (min −1 ) 20 7 × 10 2 (min −1 )
6
15
5
Time constant D/R 2 10 5 N 2 O 2 4 Time constant D/R 2
3
1
0 2
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8
Figure 5.25. Concentration-dependent diffusion time constants for O 2 and N 2 in Bergbau
◦
Forschung CMS at 27 C (Chen et al., 1994; Chen, 1994, with permission).