Page 283 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 283
268 CARBON NANOTUBES, PILLARED CLAYS, AND POLYMERIC RESINS
400
380
360
BPL
340
ACTIVATED
CARBON
320
300
280
260
Weight adsorbed (mg H 2 O/g) 220
240
200
180
160
140
120
100
XE-340
80
60
40
20
0
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Relative humidity
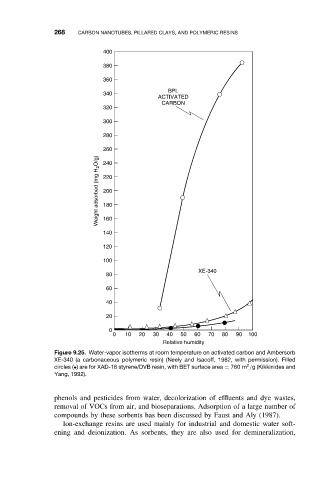
Figure 9.25. Water-vapor isotherms at room temperature on activated carbon and Ambersorb
XE-340 (a carbonaceous polymeric resin) (Neely and Isacoff, 1982, with permission). Filled
2
circles (•) are for XAD-16 styrene/DVB resin, with BET surface area = 760 m /g (Kikkinides and
Yang, 1992).
phenols and pesticides from water, decolorization of effluents and dye wastes,
removal of VOCs from air, and bioseparations. Adsorption of a large number of
compounds by these sorbents has been discussed by Faust and Aly (1987).
Ion-exchange resins are used mainly for industrial and domestic water soft-
ening and deionization. As sorbents, they are also used for demineralization,