Page 281 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 281
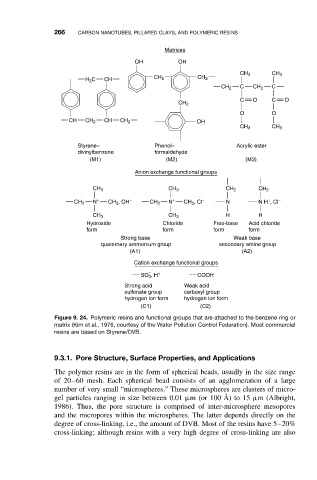
266 CARBON NANOTUBES, PILLARED CLAYS, AND POLYMERIC RESINS
Matrices
OH OH
CH 3 CH 3
H 2 C CH CH 2 CH 2
CH 2 C CH 2 C
C O C O
CH 2
O O
CH CH 2 CH CH 2 OH
CH 3 CH 3
Styrene– Phenol– Acrylic ester
divinylbenzene formaldehyde
(M1) (M2) (M3)
Anion exchange functional groups
CH 3 CH 3 CH 2 CH 2
+ − + − + −
CH 2 N CH 3 , OH CH 2 N CH 3 , Cl N N H , Cl
CH 3 CH 3 H H
Hydroxide Chloride Free-base Acid chloride
form form form form
Strong base Weak base
quaternary ammonium group secondary amine group
(A1) (A2)
Cation exchange functional groups
− +
SO 3 , H COOH
Strong acid Weak acid
sulfonate group carboxyl group
hydrogen ion form hydrogen ion form
(C1) (C2)
Figure 9. 24. Polymeric resins and functional groups that are attached to the benzene ring or
matrix (Kim et al., 1976, courtesy of the Water Pollution Control Federation). Most commercial
resins are based on Styrene/DVB.
9.3.1. Pore Structure, Surface Properties, and Applications
The polymer resins are in the form of spherical beads, usually in the size range
of 20–60 mesh. Each spherical bead consists of an agglomeration of a large
number of very small “microspheres.” These microspheres are clusters of micro-
gel particles ranging in size between 0.01 µm (or 100 ˚ A) to 15 µm (Albright,
1986). Thus, the pore structure is comprised of inter-microsphere mesopores
and the micropores within the microspheres. The latter depends directly on the
degree of cross-linking, i.e., the amount of DVB. Most of the resins have 5–20%
cross-linking; although resins with a very high degree of cross-linking are also