Page 358 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 358
NITROGEN/METHANE SEPARATION 343
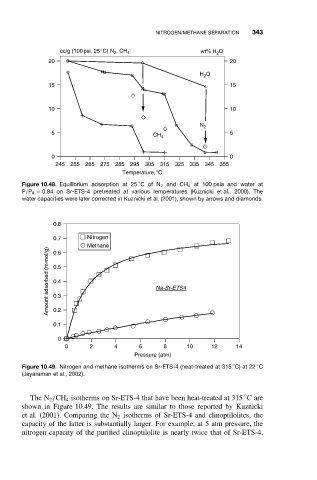
cc/g (100 psi, 25°C) N 2 , CH 4 wt% H 2 O
20 20
H 2 O
15 15
10 10
N 2
5 5
CH 4
0 0
245 255 265 275 285 295 305 315 325 335 345 355
Temperature,°C
◦
Figure 10.48. Equilibrium adsorption at 25 CofN 2 and CH 4 at 100 psia and water at
P/P 0 = 0.84 on Sr-ETS-4 pretreated at various temperatures (Kuznicki et al., 2000). The
water capacities were later corrected in Kuznicki et al. (2001), shown by arrows and diamonds.
0.8
0.7 Nitrogen
Methane
Amount adsorbed (m mol/g) 0.5 Na-Sr-ETS4
0.6
0.4
0.3
0.2
0.1
0
0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14
Pressure (atm)
Figure 10.49. Nitrogen and methane isotherms on Sr-ETS-4 (heat-treated at 315 C) at 22 C
◦
◦
(Jayaraman et al., 2002).
◦
The N 2 /CH 4 isotherms on Sr-ETS-4 that have been heat-treated at 315 Care
shown in Figure 10.49. The results are similar to those reported by Kuznicki
et al. (2001). Comparing the N 2 isotherms of Sr-ETS-4 and clinoptilolites, the
capacity of the latter is substantially larger. For example, at 5 atm pressure, the
nitrogen capacity of the purified clinoptilolite is nearly twice that of Sr-ETS-4.