Page 356 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 356
NITROGEN/METHANE SEPARATION 341
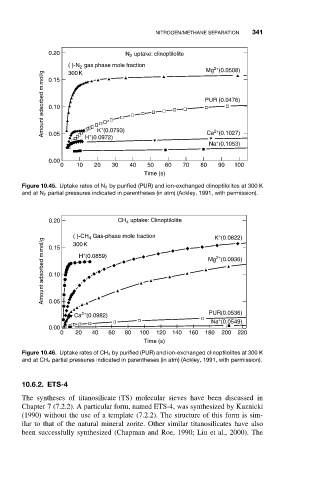
0.20 N uptake: clinoptilolite
2
( )-N gas phase mole fraction Mg (0.0508)
2
2+
Amount adsorbed m mol/g 0.10 PUR (0.0476)
300 K
0.15
+
K (0.0793)
2+
Ca (0.1027)
0.05
+
H (0.0972)
+
Na (0.1053)
0.00
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Time (s)
Figure 10.45. Uptake rates of N 2 by purified (PUR) and ion-exchanged clinoptilolites at 300 K
and at N 2 partial pressures indicated in parentheses (in atm) (Ackley, 1991, with permission).
0.20 CH uptake: Clinoptilolite
4
+
( )-CH Gas-phase mole fraction K (0.0822)
4
Amount adsorbed m mol/g 0.10 H (0.0859) Mg (0.0936)
300 K
0.15
+
2+
0.05
2+
Ca (0.0982) PUR(0.0536)
+
Na (0.0549)
0.00
0 20 40 60 80 100 120 140 160 180 200 220
Time (s)
Figure 10.46. Uptake rates of CH 4 by purified (PUR) and ion-exchanged clinoptilolites at 300 K
and at CH 4 partial pressures indicated in parentheses (in atm) (Ackley, 1991, with permission).
10.6.2. ETS-4
The syntheses of titanosilicate (TS) molecular sieves have been discussed in
Chapter 7 (7.2.2). A particular form, named ETS-4, was synthesized by Kuznicki
(1990) without the use of a template (7.2.2). The structure of this form is sim-
ilar to that of the natural mineral zorite. Other similar titanosilicates have also
been successfully synthesized (Chapman and Roe, 1990; Liu et al., 2000). The