Page 352 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 352
NITROGEN/METHANE SEPARATION 337
formula for the ideal clinoptilolite is
Na 6 Al 6 Si 30 O 72 · 24H 2 O
The unit cell is monoclinic and is usually characterized on the basis of 72 O
+
+
atoms and 24 water molecules, with Na ,K ,Ca ,and Mg 2+ as the most
2+
common charge-balancing cations. The channel structure and the cation sites of
clinoptilolite are discussed in Chapter 7 (7.4.1). It has a 2-dimensional channel
structure that is formed by 8-oxygen rings and 10-oxygen rings. The transport
channels have been discussed in detail by Ackley and Yang (1991b). The selec-
tivity and rate of uptake of gases are strongly influenced by the type, number,
and location of the cations in these channels.
Frankiewicz and Donnelly (1983) showed the promise of a calcium-exchanged
clinoptilolite for N 2 /CH 4 separation by a PSA process, but the product was below
pipeline quality. This work stimulated a good deal of interest in further investi-
gation. Two Japanese patent applications (61-255,994, in 1986, and 62-132,542
in 1987, see Chao, 1990) disclosed the use of natural clinoptilolite and Ca-
exchanged forms for nitrogen removal from methane. Chao (1990) suggested the
use of Mg-exchanged clinoptilolite for N 2 /CH 4 separation.
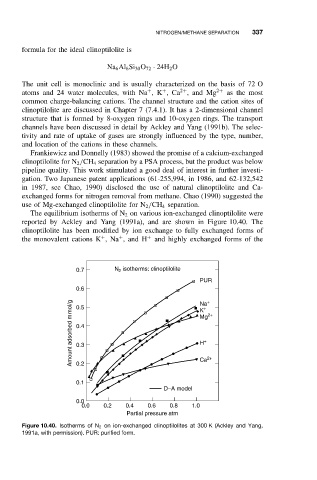
The equilibrium isotherms of N 2 on various ion-exchanged clinoptilolite were
reported by Ackley and Yang (1991a), and are shown in Figure 10.40. The
clinoptilolite has been modified by ion exchange to fully exchanged forms of
+
the monovalent cations K ,Na ,and H + and highly exchanged forms of the
+
0.7 N isotherms: clinoptilolite
2
PUR
0.6 Na +
Amount adsorbed mmol/g 0.4 Mg 2+
0.5
+
K
2+
+
H
0.3
0.2
0.1 Ca
D–A model
0.0
0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1.0
Partial pressure atm
Figure 10.40. Isotherms of N 2 on ion-exchanged clinoptilolites at 300 K (Ackley and Yang,
1991a, with permission). PUR: purified form.