Page 350 - Adsorbents fundamentals and applications
P. 350
NITROGEN/METHANE SEPARATION 335
293 K Closed symbol: ethylene
303 K
1.5 Open symbol: ethane
313 K
333 K
363 K
303 K Ethylene (unsupported clay)
303 K Ethane (unsupported clay)
1.0
A
q, m mol/g
0.5
B
0.0
0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200
p, mmHg
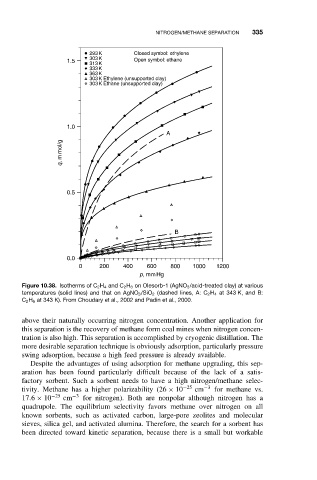
Figure 10.38. Isotherms of C 2 H 4 and C 2 H 6 on Olesorb-1 (AgNO 3 /acid-treated clay) at various
temperatures (solid lines) and that on AgNO 3 /SiO 2 (dashed lines, A: C 2 H 4 at 343 K, and B:
C 2 H 6 at 343 K). From Choudary et al., 2002 and Padin et al., 2000.
above their naturally occurring nitrogen concentration. Another application for
this separation is the recovery of methane form coal mines when nitrogen concen-
tration is also high. This separation is accomplished by cryogenic distillation. The
more desirable separation technique is obviously adsorption, particularly pressure
swing adsorption, because a high feed pressure is already available.
Despite the advantages of using adsorption for methane upgrading, this sep-
aration has been found particularly difficult because of the lack of a satis-
factory sorbent. Such a sorbent needs to have a high nitrogen/methane selec-
tivity. Methane has a higher polarizability (26 × 10 −25 cm −3 for methane vs.
17.6 × 10 −25 cm −3 for nitrogen). Both are nonpolar although nitrogen has a
quadrupole. The equilibrium selectivity favors methane over nitrogen on all
known sorbents, such as activated carbon, large-pore zeolites and molecular
sieves, silica gel, and activated alumina. Therefore, the search for a sorbent has
been directed toward kinetic separation, because there is a small but workable