Page 125 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 125
Chapter 6. ‘Wet’ gas turbine plants 91
0.7
0.6
+ 0.5
0
z
w
2 0.4
L
L +EFFICIENCY [CBliXr DRY
W
4
+- EFFICIENCY [CBTIiXr WET
2 Oa3
W
>
0 0.2 -A- MASS OF WATER INJECTED
FRACTION OF AIR FLO
0.1
0
1 3 5 7 9 11 13 15
PRESSURE RATIO
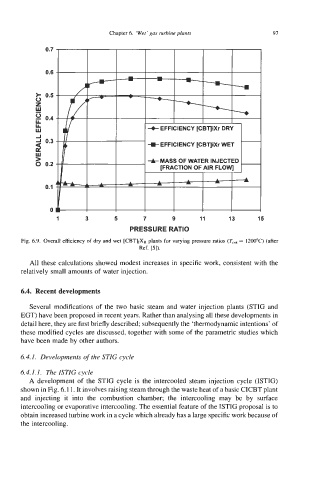
Fig. 6.9. Overall efficiency of dry and wet [CBTIIXR plants for varying pressure ratios (Tcm = 1200°C) (after
Ref. IS]).
All these calculations showed modest increases in specific work, consistent with the
relatively small amounts of water injection.
6.4. Recent developments
Several modifications of the two basic steam and water injection plants (STIG and
EGT) have been proposed in recent years. Rather than analysing all these developments in
detail here, they are first briefly described; subsequently the ‘thermodynamic intentions’ of
these modified cycles are discussed, together with some of the parametric studies which
have been made by other authors.
6.4.1. Developments of the STIG cycle
6.4.1.1. The ISTIG cycle
A development of the STIG cycle is the intercooled steam injection cycle (ISTIG)
shown in Fig. 6.1 1. It involves raising steam through the waste heat of a basic CICBT plant
and injecting it into the combustion chamber; the intercooling may be by surface
intercooling or evaporative intercooling. The essential feature of the ISTIG proposal is to
obtain increased turbine work in a cycle which already has a large specific work because of
the intercooling.