Page 185 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 185
Chapter 8. Novel gas turbine cycles 151
ABSORPTION,
C02 FREE EXHAUST
EXCHANGER
EXHAUST TO
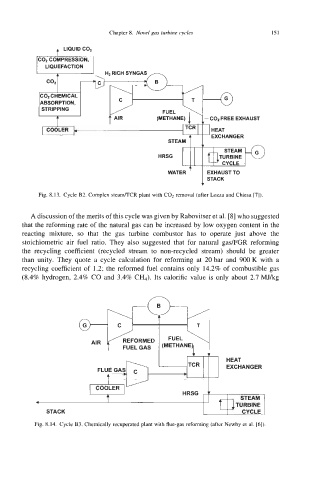
Fig. 8.13. Cycle 92. Complex steam/TCR plant with COl removal (after Lozza and Chiesa [7]).
A discussion of the merits of this cycle was given by Rabovitser et al. [8] who suggested
that the reforming rate of the natural gas can be increased by low oxygen content in the
reacting mixture, so that the gas turbine combustor has to operate just above the
stoichiometric air fuel ratio. They also suggested that for natural gas/FGR reforming
the recycling coefficient (recycled stream to non-recycled stream) should be greater
than unity. They quote a cycle calculation for reforming at 20 bar and 900K with a
recycling coefficient of 1.2; the reformed fuel contains only 14.2% of combustible gas
(8.4% hydrogen, 2.4% CO and 3.4% Ch). Its calorific value is only about 2.7 MJkg
STEAM
TURBINE
STACK L w CYCLE
Fig. 8.14. Cycle B3. Chemically recuperated plant with flue-gas reforming (after Newby et al. [SI).