Page 186 - Advanced Gas Turbine Cycles
P. 186
I52 Advanced gas turbine cycles
compared with 50MJkg for methane itself, but of course there is now an even larger
flow of combustible gas that goes to the combustor so the ‘heating value’ is slightly
increased.
In another example Newby et al. [6] calculated a cycle with the reformer operating at
comparable pressure and temperature but with a higher recycling rate of 1.7, leading to a
conversion rate of a = 0.56 (this is closer to the conversion rate of Lloyd’s steam/TCR
cycle, a = 0.373, described in the last section). A thermal efficiency of 38.7% is claimed
for this FG/TCR cycle, slightly greater than the simple CBT cycle efficiency of 35.7% but
much less than the calculated efficiency for the steam/TCR cycle (48.7%) and a
comparable STIG cycle (45.6%).
Clearly, these figures suggest that the plant is very sensitive to the amount of flue gas
recycled. There appears to be no full parametric or economic calculation published in the
literature for this FG/TCR cycle, which suggests that it has not been considered as an
attractive option.
8.6.3. Cycles C burning non-carbon fuel (hydrogen)
Obviously, use of a non-carbon fuel-usually containing hydrogen4bviates the need
for any carbon dioxide extraction and disposal. These cycles are listed in Table 8. lC, and
the associated Figs. 8.15-8.17.
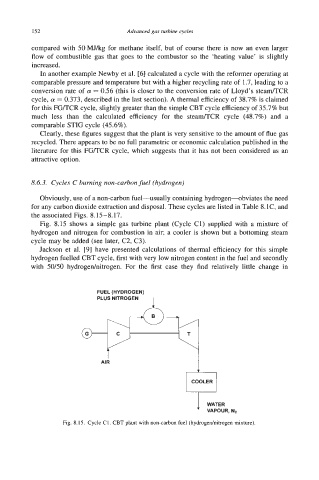
Fig. 8.15 shows a simple gas turbine plant (Cycle C1) supplied with a mixture of
hydrogen and nitrogen for combustion in air; a cooler is shown but a bottoming steam
cycle may be added (see later, C2, C3).
Jackson et al. [9] have presented calculations of thermal efficiency for this simple
hydrogen fuelled CBT cycle, first with very low nitrogen content in the fuel and secondly
with 50/50 hydrogednitrogen. For the first case they find relatively little change in
FUEL (HYDROGEN)
A
PLUS NITROGEN
AIR
COOLER
WATER
VAPOUR, N2
Fig. 8.15. Cycle C1. CBT plant with non-carbon fuel (hydrogednitrogen mixture).