Page 1021 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 1021
1005
SECTION 11.2
Characteristics of
Reactions Involving
Radical Intermediates
Donor-substituted Acceptor-substituted SOMO Acceptor-substituted Donor-substituted SOMO
alkene is more is lowered in energy and alkene is more is raised in energy and
nucleophilic radical is more electrophilic electrophilic radical is more nucleophilic
Fig. 11.6. Frontier orbital interactions between different combinations of substituted radicals and alkenes
showing enhanced interaction relative to unsubstituted systems.
the radical site is substituted by an electron-attracting group, the SOMO is lower.
A complementary interaction between the radical and alkene is possible.
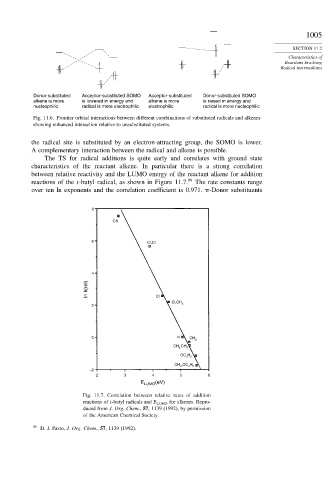
The TS for radical additions is quite early and correlates with ground state
characteristics of the reactant alkene. In particular there is a strong correlation
between relative reactivity and the LUMO energy of the reactant alkene for addition
reactions of the t-butyl radical, as shown in Figure 11.7. 99 The rate constants range
over ten ln exponents and the correlation coefficient is 0.971. -Donor substituents
8
CN
6 Cl,Cl
4
In k(rel) Cl
Cl,CH 3
2
0 H
CH 3,
CH 3, CH 5
OC 2 H 5
CH 3 ,OC 2 H 5
–2
2 3 4 5 6
E LUMO (eV)
Fig. 11.7. Correlation between relative rates of addition
reactions of t-butyl radicals and E LUMO for alkenes. Repro-
duced from J. Org. Chem., 57, 1139 (1992), by permission
of the American Chemical Society.
99
D. J. Pasto, J. Org. Chem., 57, 1139 (1992).