Page 134 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 134
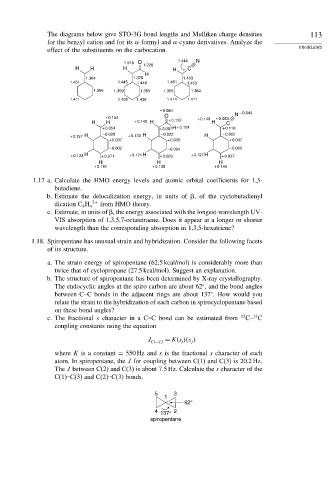
The diagrams below give STO-3G bond lengths and Mulliken charge densities 113
for the benzyl cation and for its -formyl and -cyano derivatives. Analyze the
PROBLEMS
effect of the substituents on the carbocation.
1.518 O 1.226 1.444 N
H H H H C
H
1.364 1.378 1.453
1.451 1.445 1.448 1.451 1.453
1.366 1.369 1.365 1.365 1.364
1.411 1.435 1.438 1.414 1.411
– 0.084 – 0.044
O N
+ 0.154 + 0.149 + 0.083
H H + 0.149 H + 0.133 H C
+ 0.054 + 0.097 H + 0.104 + 0.110
+ 0.127 H – 0.020 + 0.133 H – 0.022 H – 0.002
+ 0.037 + 0.035 + 0.037
– 0.062 – 0.064 – 0.062
+ 0.123 H + 0.071 + 0.121 H + 0.063 + 0.127 H + 0.037
H H H
+ 0.141 + 0.138 + 0.144
1.17 a. Calculate the HMO energy levels and atomic orbital coefficients for 1,3-
butadiene.
b. Estimate the delocalization energy, in units of , of the cyclobutadienyl
dication C H 2+ from HMO theory.
4 4
c. Estimate, in units of , the energy associated with the longest-wavelength UV-
VIS absorption of 1,3,5,7-octatetraene. Does it appear at a longer or shorter
wavelength than the corresponding absorption in 1,3,5-hexatriene?
1.18. Spiropentane has unusual strain and hybridization. Consider the following facets
of its structure.
a. The strain energy of spiropentane (62.5 kcal/mol) is considerably more than
twice that of cyclopropane (27.5 kcal/mol). Suggest an explanation.
b. The structure of spiropentane has been determined by X-ray crystallography.
The endocyclic angles at the spiro carbon are about 62 , and the bond angles
between C–C bonds in the adjacent rings are about 137 . How would you
relate the strain to the hybridization of each carbon in spirocyclopentane based
on these bond angles?
13
c. The fractional s character in a C–C bond can be estimated from 13 C– C
coupling constants using the equation
J = K s s
Ci−Cj i j
where K is a constant = 550 Hz and s is the fractional s character of each
atom. In spiropentane, the J for coupling between C(1) and C(3) is 20.2 Hz.
The J between C(2) and C(3) is about 7.5 Hz. Calculate the s character of the
C(1)–C(3) and C(2)–C(3) bonds.
5 3
1
62°
4 137° 2
spiropentane