Page 135 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 135
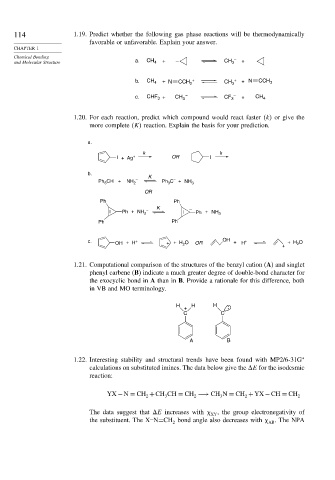
114 1.19. Predict whether the following gas phase reactions will be thermodynamically
favorable or unfavorable. Explain your answer.
CHAPTER 1
Chemical Bonding –
and Molecular Structure a. CH 4 + – CH 3 +
b. CH 4 + N CCH 2 + CH 3 + + N CCH 3
c. CHF + CH 3 – CF 3 – + CH 4
3
1.20. For each reaction, predict which compound would react faster k or give the
more complete K reaction. Explain the basis for your prediction.
a.
k k
I + Ag + OR I
b. K
–
CH + NH – Ph C + NH
Ph 3 2 3 3
OR
Ph Ph
K
Ph + NH 2 – – Ph + NH 3
Ph Ph
c. OH + H + O OR OH + H + O
+ + H 2
+ + H 2
1.21. Computational comparison of the structures of the benzyl cation (A) and singlet
phenyl carbene (B) indicate a much greater degree of double-bond character for
the exocyclic bond in A than in B. Provide a rationale for this difference, both
in VB and MO terminology.
H H H
+
C C
A B
1.22. Interesting stability and structural trends have been found with MP2/6-31G ∗
calculations on substituted imines. The data below give the
E for the isodesmic
reaction:
YX −N = CH +CH CH = CH −→ CH N = CH +YX −CH = CH 2
2
2
3
3
2
The data suggest that
E increases with , the group electronegativity of
XY
the substituent. The X–N=CH bond angle also decreases with . The NPA
AB
2