Page 136 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 136
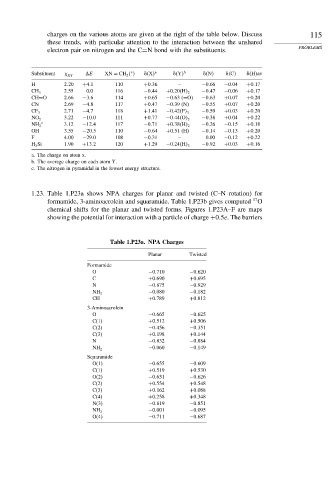
charges on the various atoms are given at the right of the table below. Discuss 115
these trends, with particular attention to the interaction between the unshared
electron pair on nitrogen and the C=N bond with the substituents. PROBLEMS
Substituent XY
E XN = CH 2 & X a & Y b & N & C & H av
H 2 20 +4 1 110 +0 36 – −0 66 −0 04 +0 17
2 55 0.0 116 −0 44 −0 47 −0 06 +0 17
CH 3 +0 20 H 2
CH=O 2 66 −3 6 114 +0 65 −0 63 (=O) −0 63 +0 07 +0 20
CN 2 69 −4 8 117 +0 47 −0 39 (N) −0 55 +0 07 +0 20
2 71 −4 7 118 +1 41 −0 59 +0 03 +0 20
CF 3 −0 42 F 3
3 22 −10 0 111 +0 77 −0 38 +0 04 +0 22
NO 2 −0 44 O 2
c
NH 2 3 12 −12 4 117 −0 71 +0 38 H 2 −0 26 −0 15 +0 18
OH 3 55 −20 5 110 −0 64 +0 51 (H) −0 14 −0 13 +0 20
F 4 00 −29 0 108 −0 31 – 0.00 −0 12 +0 22
H 3 Si 1 90 +13 2 120 +1 29 −0 24 H 3 −0 92 +0 03 +0 16
a. The charge on atom x.
b. The average charge on each atom Y.
c. The nitrogen in pyramidal in the lowest energy structure.
1.23. Table 1.P23a shows NPA charges for planar and twisted (C–N rotation) for
17
formamide, 3-aminoacrolein and squaramide. Table 1.P23b gives computed O
chemical shifts for the planar and twisted forms. Figures 1.P23A–F are maps
showing the potential for interaction with a particle of charge +0 5e. The barriers
Table 1.P23a. NPA Charges
Planar Twisted
Formamide
O −0 710 −0 620
C +0 690 +0 695
N −0 875 −0 929
−0 080 −0 182
NH 2
CH +0 789 +0 812
3-Aminoacrolein
O −0 665 −0 625
C(1) +0 512 +0 506
C(2) −0 456 −0 351
C(3) +0 198 +0 144
N −0 832 −0 884
−0 060 −0 149
NH 2
Squaramide
O(1) −0 655 −0 609
C(1) +0 519 +0 530
O(2) −0 631 −0 626
C(2) +0 554 +0 548
C(3) +0 162 +0 088
C(4) +0 258 +0 348
N(3) −0 819 −0 851
−0 001 −0 095
NH 2
O(4) −0 711 −0 687