Page 132 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 132
analyze the relative importance of intrinsic anion stabilization and solvation on 111
the observed acidity.
PROBLEMS
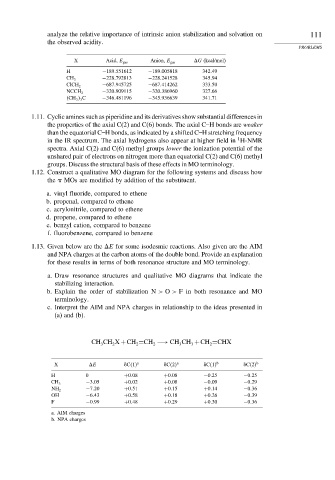
X Acid, E gas Anion, E gas
G (kcal/mol)
H −189 551612 −189 005818 342 49
−228 792813 −228 241528 345 94
CH 3
−687 945725 −687 414262 333 50
ClCH 2
−320 909115 −320 386960 327 66
NCCH 2
CH 3 3 C −346 481196 −345 936639 341 71
1.11. Cyclic amines such as piperidine and its derivatives show substantial differences in
the properties of the axial C(2) and C(6) bonds. The axial C–H bonds are weaker
than the equatorial C–H bonds, as indicated by a shifted C–H stretching frequency
1
in the IR spectrum. The axial hydrogens also appear at higher field in H-NMR
spectra. Axial C(2) and C(6) methyl groups lower the ionization potential of the
unshared pair of electrons on nitrogen more than equatorial C(2) and C(6) methyl
groups. Discuss the structural basis of these effects in MO terminology.
1.12. Construct a qualitative MO diagram for the following systems and discuss how
the MOs are modified by addition of the substituent.
a. vinyl fluoride, compared to ethene
b. propenal, compared to ethene
c. acrylonitrile, compared to ethene
d. propene, compared to ethene
e. benzyl cation, compared to benzene
f. fluorobenzene, compared to benzene
1.13. Given below are the
E for some isodesmic reactions. Also given are the AIM
and NPA charges at the carbon atoms of the double bond. Provide an explanation
for these results in terms of both resonance structure and MO terminology.
a. Draw resonance structures and qualitative MO diagrams that indicate the
stabilizing interaction.
b. Explain the order of stabilization N > O > F in both resonance and MO
terminology.
c. Interpret the AIM and NPA charges in relationship to the ideas presented in
(a) and (b).
CH CH X +CH =CH −→ CH CH +CH =CHX
2
2
3
3
2
2
3
X
E &C 1 a &C 2 a &C 1 b &C 2 b
H 0 +0 08 +0 08 −0 25 −0 25
−3 05 +0 02 +0 08 −0 09 −0 29
CH 3
−7 20 +0 51 +0 15 +0 14 −0 36
NH 2
OH −6 43 +0 58 +0 18 +0 26 −0 39
F −0 99 +0 48 +0 29 +0 30 −0 36
a. AIM charges
b. NPA charges