Page 129 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 129
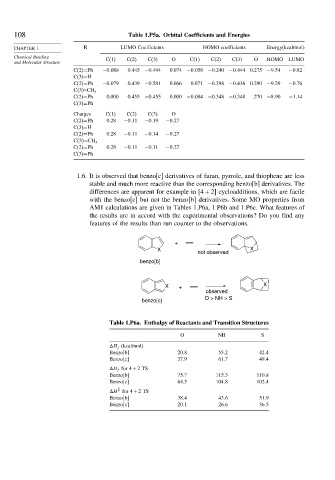
108 Table 1.P5a. Orbital Coefficients and Energies
CHAPTER 1 R LUMO Coefficients HOMO coefficients Energy(kcal/mol)
Chemical Bonding C(1) C(2) C(3) O C(1) C(2) C(3) O HOMO LUMO
and Molecular Structure
C(2)=Ph −0 088 0.445 −0 494 0.074 −0 058 −0 240 −0 444 0.275 −9 54 −0 82
C(3)=H
C(2)=Ph −0 079 0.439 −0 501 0.066 0.071 −0 298 −0 436 0.290 −9 29 −0 76
C 3 =CH 3
C(2)=Ph 0.000 0.455 −0 455 0.000 −0 084 −0 348 −0 348 .270 −8 90 −1 14
C(3)=Ph
Charges C(1) C(2) C(3) O
C(2)=Ph 0.28 −0 11 −0 19 −0 27
C(3)=H
C(2)=Ph 0.28 −0 11 −0 14 −0 27
C 3 =CH 3
C(2)=Ph 0.28 −0 11 −0 11 −0 27
C(3)=Ph
1.6. It is observed that benzo[c] derivatives of furan, pyrrole, and thiophene are less
stable and much more reactive than the corresponding benzo[b] derivatives. The
differences are apparent for example in 4+2 cycloadditions, which are facile
with the benzo[c] but not the benzo[b] derivatives. Some MO properties from
AM1 calculations are given in Tables 1.P6a, 1.P6b and 1.P6c. What features of
the results are in accord with the experimental observations? Do you find any
features of the results than run counter to the observations.
+
X X
not observed
benzo[b]
X + X
observed
O > NH > S
benzo[c]
Table 1.P6a. Enthalpy of Reactants and Transition Structures
O NH S
H f (kcal/mol)
Benzo[b] 20 8 55 2 42 4
Benzo[c] 27 9 61 7 49 4
H f for 4+2TS
Benzo[b] 75 7 115 3 110 8
Benzo[c] 64 5 104 8 102 4
‡
H for 4+2TS
Benzo[b] 38 4 43 6 51 9
Benzo[c] 20 1 26 6 36 5