Page 195 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 195
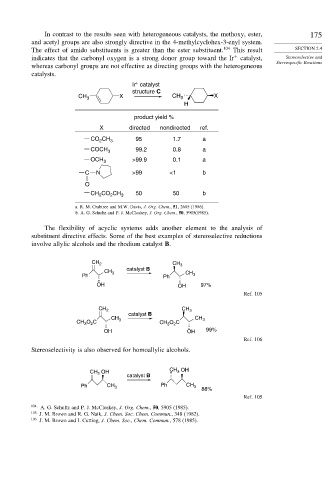
In contrast to the results seen with heterogeneous catalysts, the methoxy, ester, 175
and acetyl groups are also strongly directive in the 4-methylcyclohex-3-enyl system.
The effect of amido substituents is greater than the ester substituent. 104 This result SECTION 2.4
+
indicates that the carbonyl oxygen is a strong donor group toward the Ir catalyst, Stereoselective and
Stereospecific Reactions
whereas carbonyl groups are not effective as directing groups with the heterogeneous
catalysts.
+
Ir catalyst
structure C
CH 3 X CH 3 X
H
product yield %
X directed nondirected ref.
CO CH 3 95 1.7 a
2
COCH 3 99.2 0.8 a
OCH 3 >99.9 0.1 a
C N >99 <1 b
O
CH CO CH 3 50 50 b
2
2
a. R. M. Crabtree and M.W. Davis, J. Org. Chem., 51, 2685 (1986).
b. A. G. Schultz and P. J. McCloskey, J. Org. Chem., 50, 5905(1985).
The flexibility of acyclic systems adds another element to the analysis of
substituent directive effects. Some of the best examples of stereoselective reductions
involve allylic alcohols and the rhodium catalyst B.
CH 2 CH 3
catalyst B
CH 3 CH
Ph Ph 3
OH OH 97%
Ref. 105
CH 2 CH 3
catalyst B
CH CH 3
CH O C 3 CH 3 O C
2
3
2
OH OH 99%
Ref. 106
Stereoselectivity is also observed for homoallylic alcohols.
OH
OH CH 3
CH 2
catalyst B
Ph CH 3 Ph CH 3 88%
Ref. 105
104 A. G. Schultz and P. J. McCloskey, J. Org. Chem., 50, 5905 (1985).
105 J. M. Brown and R. G. Naik, J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun., 348 (1982).
106
J. M. Brown and I. Cutting, J. Chem. Soc., Chem. Commun., 578 (1985).