Page 358 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 358
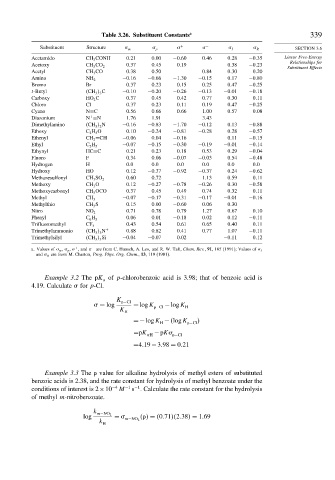
Table 3.26. Substituent Constants a 339
Substituent Structure m p + − I R SECTION 3.6
Acetamido CH 3 CONH 0 21 0 00 −0 60 0 46 0 28 −0 35 Linear Free-Energy
Relationships for
Acetoxy CH 3 CO 2 0 37 0 45 0 19 0 38 −0 23
Substituent Effects
Acetyl CH 3 CO 0 38 0 50 0 84 0 30 0 20
Amino NH 2 −0 16 −0 66 −1 30 −0 15 0 17 −0 80
Bromo Br 0 37 0 23 0 15 0 25 0 47 −0 25
t-Butyl CH 3 3 C −0 10 −0 20 −0 26 −0 13 −0 01 −0 18
Carboxy HO 2 C 0 37 0 45 0 42 0 77 0 30 0 11
Chloro Cl 0 37 0 23 0 11 0 19 0 47 −0 25
Cyano N≡C 0 56 0 66 0 66 1 00 0 57 0 08
+
Diazonium N ≡N 1 76 1 91 3 43
Dimethylamino CH 3 2 N −0 16 −0 83 −1 70 −0 12 0 13 −0 88
Ethoxy C 2 H 5 O 0 10 −0 24 −0 81 −0 28 0 28 −0 57
Ethenyl CH 2 =CH −0 06 0 04 −0 16 0 11 −0 15
Ethyl C 2 H 5 −0 07 −0 15 −0 30 −0 19 −0 01 −0 14
Ethynyl HC≡C 0 21 0 23 0 18 0 53 0 29 −0 04
Fluoro F 0 34 0 06 −0 07 −0 03 0 54 −0 48
Hydrogen H 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Hydroxy HO 0 12 −0 37 −0 92 −0 37 0 24 −0 62
Methanesulfonyl CH 3 SO 2 0 60 0 72 1 13 0 59 0 11
Methoxy CH 3 O 0 12 −0 27 −0 78 −0 26 0 30 −0 58
Methoxycarbonyl CH 3 OCO 0 37 0 45 0 49 0 74 0 32 0 11
Methyl CH 3 −0 07 −0 17 −0 31 −0 17 −0 01 −0 16
Methylthio CH 3 S 0 15 0 00 −0 60 0 06 0 30
Nitro NO 2 0 71 0 78 0 79 1 27 0 67 0 10
Phenyl C 6 H 5 0 06 0 01 −0 18 0 02 0 12 −0 11
Trifluoromethyl CF 3 0 43 0 54 0 61 0 65 0 40 0 11
Trimethylammonio CH 3 3 N + 0 88 0 82 0 41 0 77 1 07 −0 11
Trimethylsilyl CH 3 3 Si −0 04 −0 07 0 02 −0 11 0 12
+ −
a. Values of m , p , , and are from C. Hansch, A. Leo, and R. W. Taft, Chem. Rev., 91, 165 (1991); Values of I
and R are from M. Charton, Prog. Phys. Org. Chem., 13, 119 (1981).
Example 3.2 The pK of p-chlorobenzoic acid is 3.98; that of benzoic acid is
a
4.19. Calculate for p-Cl.
K −Cl
= log =logK −Cl −logK H
K
H
=−logK − logK −Cl
H
=pK H −pK −Cl
=4 19−3 98 = 0 21
Example 3.3 The value for alkaline hydrolysis of methyl esters of substituted
benzoic acids is 2.38, and the rate constant for hydrolysis of methyl benzoate under the
conditions of interest is 2×10 −4 M −1 −1
s . Calculate the rate constant for the hydrolysis
of methyl m-nitrobenzoate.
k
log m−NO 2 = = 0 71 2 38 = 1 69
k H m−NO 2