Page 360 - Advanced Organic Chemistry Part A - Structure and Mechanisms, 5th ed (2007) - Carey _ Sundberg
P. 360
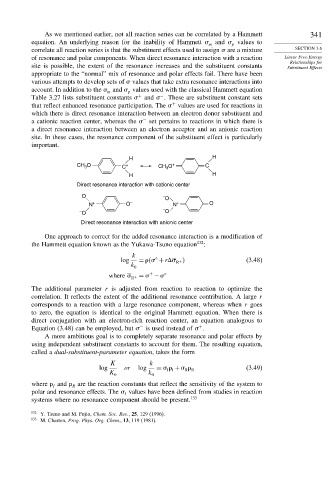
As we mentioned earlier, not all reaction series can be correlated by a Hammett 341
equation. An underlying reason for the inability of Hammett and values to
m p
correlate all reaction series is that the substituent effects used to assign are a mixture SECTION 3.6
of resonance and polar components. When direct resonance interaction with a reaction Linear Free-Energy
Relationships for
site is possible, the extent of the resonance increases and the substituent constants Substituent Effects
appropriate to the “normal” mix of resonance and polar effects fail. There have been
various attempts to develop sets of values that take extra resonance interactions into
account. In addition to the and values used with the classical Hammett equation
m p
−
+
Table 3.27 lists substituent constants and . These are substituent constant sets
+
that reflect enhanced resonance participation. The values are used for reactions in
which there is direct resonance interaction between an electron donor substituent and
−
a cationic reaction center, whereas the set pertains to reactions in which there is
a direct resonance interaction between an electron acceptor and an anionic reaction
site. In these cases, the resonance component of the substituent effect is particularly
important.
H H
CH O C + CH 3 O + C
3
H H
Direct resonance interaction with cationic center
O – O
N + O – N + O
–
– O O
Direct resonance interaction with anionic center
One approach to correct for the added resonance interaction is a modification of
the Hammett equation known as the Yukawa-Tsuno equation 132 :
k
log = +r (3.48)
R +
k
0
+
where R + = −
The additional parameter r is adjusted from reaction to reaction to optimize the
correlation. It reflects the extent of the additional resonance contribution. A large r
corresponds to a reaction with a large resonance component, whereas when r goes
to zero, the equation is identical to the original Hammett equation. When there is
direct conjugation with an electron-rich reaction center, an equation analogous to
+
Equation (3.48) can be employed, but is used instead of .
−
A more ambitious goal is to completely separate resonance and polar effects by
using independent substituent constants to account for them. The resulting equation,
called a dual-substituent-parameter equation, takes the form
K k
log or log = + (3.49)
R R
I I
K 0 k 0
where and are the reaction constants that reflect the sensitivity of the system to
I
R
polar and resonance effects. The values have been defined from studies in reaction
I
systems where no resonance component should be present. 133
132 Y. Tsuno and M. Fujio, Chem. Soc. Rev., 25, 129 (1996).
133
M. Charton, Prog. Phys. Org. Chem., 13, 119 (1981).